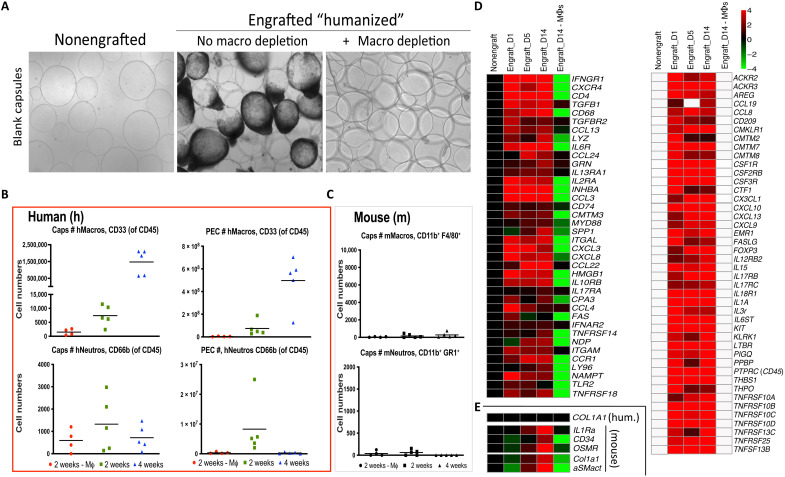
Fig. 2. FBR human macrophage dependence and mouse fibroblast cross-talk in NSG-SGM3 BLT humanized model.
(A) As compared to nonfibrosed (nonengrafted) and fibrosed (engrafted) controls, clodrosome depletion of human macrophages resulted in complete loss of fibrosis on 500-μm-diameter SLG20 alginate spheres following 2-week IP implantations in engrafted NSG-SGM3 BLT mice. (B) Flow cytometry analysis of human immune cell numbers (#) dissociated from capsule spheres (Caps) or PECs retrieved 2 or 4 weeks after IP implantation (green versus blue, respectively) showing significant increases of human (h)CD45+CD3−CD20−CD33+ myeloid cells, which were eliminated following clodrosome macrophage (Mϕ) depletion throughout 2-week implantations (red). By comparison, human neutrophils (CD45+CD66b+) did not significantly change. (C) As compared to very high absolute human immune cell numbers [in (B)], effective mouse immune cell elimination by irradiation was confirmed by low counts of residual mouse (m) macrophages (F4/80+CD11b+) and neutrophils (Ly6g+CD11b+), with no significant response by either population to material implantation or macrophage depletion. (D) NanoString analysis of cell and cytokine markers on alginate spheres at 1, 5, and 14 days after implantation in engrafted NSG-SGM3 BLT mice versus non-engrafted and engrafted but macrophage-depleted controls. Similar to wild-type FBR, macrophage and B cell markers were some of the largest dynamic responders. White, within background of the assay. (E) No human collagen was observed; instead, delayed mouse αSMactin fibroblast and collagen (Col1a1) expression indicated mouse myofibroblast engagement. For all, n = 5 (biologic replicates) per treatment. Flow cytometry was performed twice, and NanoString was performed once. For flow comparisons, one-way ANOVA (***P < 0.0001 versus clodrosome-depleted controls) was used. For NanoString, log2 scale was used; for statistical analysis, see Materials and Methods.