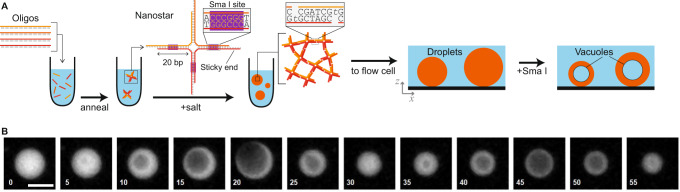
Fig. 1. Experimental overview.
A Multi-armed DNA nanostar particles, containing a restriction enzyme cleavage site in the arms, are assembled by annealing a solution of DNA oligomers, one of which carries a fluorophore. The nanostars are induced to form droplets by raising the solution salt concentration. Droplets are transferred to a flow cell, then cleavage is instigated by adding the enzyme, which causes both droplet shrinkage and the appearance of vacuoles, as revealed by fluorescent microscopy. Schematic adapted from ref. 20. B Representative images from a time-lapse acquisition showing a droplet of nanostars undergoing two cycles of vacuole growth and popping due to the action of the enzyme Sma I; see also Supplementary Movie 1. Each image is labeled with the time in minutes; scale bar 40 μm.