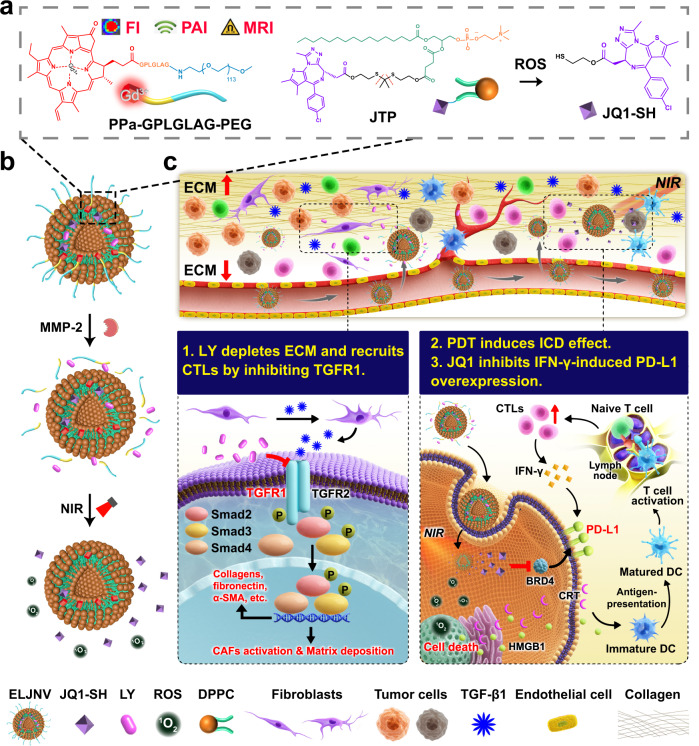
Fig. 1. Schematic of the nanovesicles to avoid the immune resistance of immune-excluded tumors (IETs).
a The chemical structure of the nanovesicles integrating a phospholipid prodrug of JQ1, photosensitizer pyropheophorbide a (PPa), and transforming growth factor β receptor 1 (TGFR1) inhibitor LY2157299 (LY). b Schematic illustration of the cascade drug release of the nanovesicles. Matrix metallopeptidase-2 (MMP-2) cleaved the poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) corona and induced the LY release. PPa generated singlet oxygen upon near-infrared (NIR) laser irradiation to release JQ1-SH. c Diagram illustrating the mechanism of the nanovesicles to overcome immune resistance. The nanovesicles (ELJNV) breach the physical barrier and enhance the tumor-specific immune response upon the 671 nm laser irradiation to overcome the intrinsic immune resistance and simultaneously suppress the interferon-γ (IFN-γ)-induced inducible immune resistance in vivo. FI fluorescence imaging, PAI photoacoustic imaging, MRI nuclear magnetic resonance imaging, ROS reactive oxygen species, ECM extracellular matrix, CTLs cytotoxic T lymphocytes, α-SMA α-smooth muscle actin, PDT photodynamic therapy, ICD immunogenic cell death, PD-L1 programmed cell death 1, BRD4 bromodomain-containing protein 4, HMGB1 high mobility group box protein 1, CRT calreticulin, DC dendritic cell, CAFs cancer-associated fibroblasts, DPPC 1,2-dipalmitoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine, JTP JQ1-thioketal (TK)-pPC, TGF-β1 transforming growth factor β1, 1O2 singlet oxygen, Gd3+ gadolinium ion.