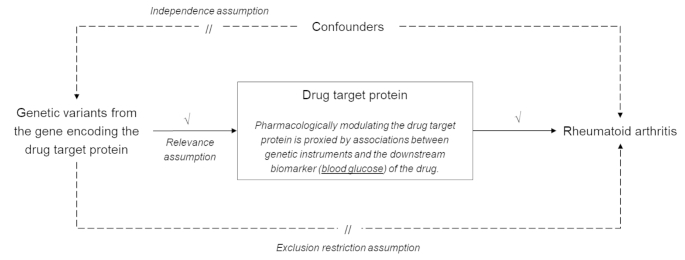
Fig. 1.
Overview of the Mendelian randomization study design. The Mendelian randomization (MR) design uses alleles randomized at germ cell formation and conception as instruments to estimate unconfounded associations between an exposure and an outcome, and can be a viable method to gauge the potential of drug repurposing. This study selects genetic variants from the gene(s) encoding the target protein(s) of the antidiabetic drug as instruments. The main downstream effect of antidiabetic drugs is decreased glucose concentration. Hence, this study leverages associations of the selected genetic instruments with blood glucose concentration to proxy the pharmacological modulation of the drug target protein of interest (relevance assumption). Genetic variants are expected to not be associated with confounders (independence assumption) and affect RA through other pathways (exclusion restriction assumption). The two samples used in the analyses were summary data from genome-wide association studies on blood glucose (UK Biobank) and clinically diagnosed RA.