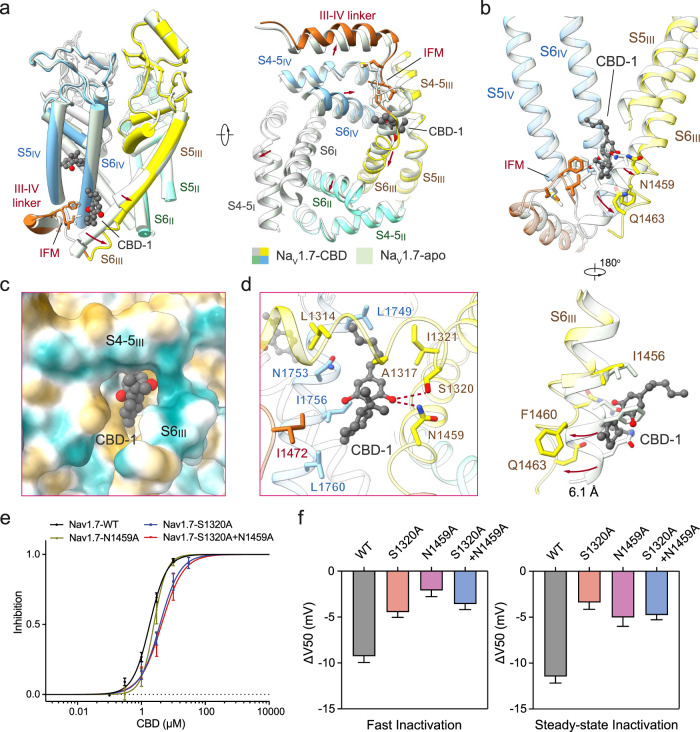
Fig. 3. Conformational changes of Nav1.7 upon CBD binding to the I-site.
a CBD binding to the I-site induces pronounced conformational shift of the PD. A side view (left) and a bottom view (right) of the superimposed PD of CBD-bound (domain colored) and apo (pale green, PDB: 7W9K) Nav1.7 are shown. CBD molecules are shown as grey spheres. The IFM motifs are shown as sticks, and the conformational changes are indicated with red arrows. b Rearrangement of the IFM binding site and surrounding elements upon CBD binding. Displacement of the corresponding residues upon CBD binding is indicated by red arrows. An enlarged view of the conformational shift of S6III is shown at the bottom. c CBD binds to a hydrophobic pocket in the I-site. The surrounding environment is shown as the hydrophobic surface, calculated in ChimeraX65. d CBD coordination in the I-site. Surrounding residues are shown as sticks. Potential hydrogen bonds are shown as red dashed lines. e Mutations at the I-site modify CBD inhibition. Two single point mutations S1320A and N1459A and a double mutation S1320A/N1459A reduced the sensitivity of Nav1.7 to CBD, with the IC50 shifted from 1.82 ± 0.10 μM to 3.81 ± 0.42 μM, 2.46 ± 0.28 μM, and 4.28 ± 0.67 μM, respectively. Nav1.7-WT, n = 1, 5, 12, 8, 7. Nav1.7-S1320A, n = 3, 5, 5, 2. Nav1.7-N1459A, n = 3, 9, 7, 5. Nav1.7-S1320A + N1459A, n = 7, 7, 4. f Mutations at I-site residues modify shifts in fast (50-ms prepulses) and steady-state inactivation (5-s prepulses) induced by 1 μM CBD. The ΔV50 values for fast inactivation: −9.26 ± 0.69 mV (WT), −4.46 ± 0.57 mV (S1320A), −2.09 ± 0.69 mV (N1459A), and −3.58 ± 0.61 mV (S1320A + N1459A); for steady-state inactivation: −11.46 ± 0.72 mV (WT), −3.39 ± 0.75 mV (S1320A), −5.02 ± 0.98 mV (N1459A) and −4.76 ± 0.52 mV (S1320A + N1459A). Data represent mean ± SEM. n biological independent cells.