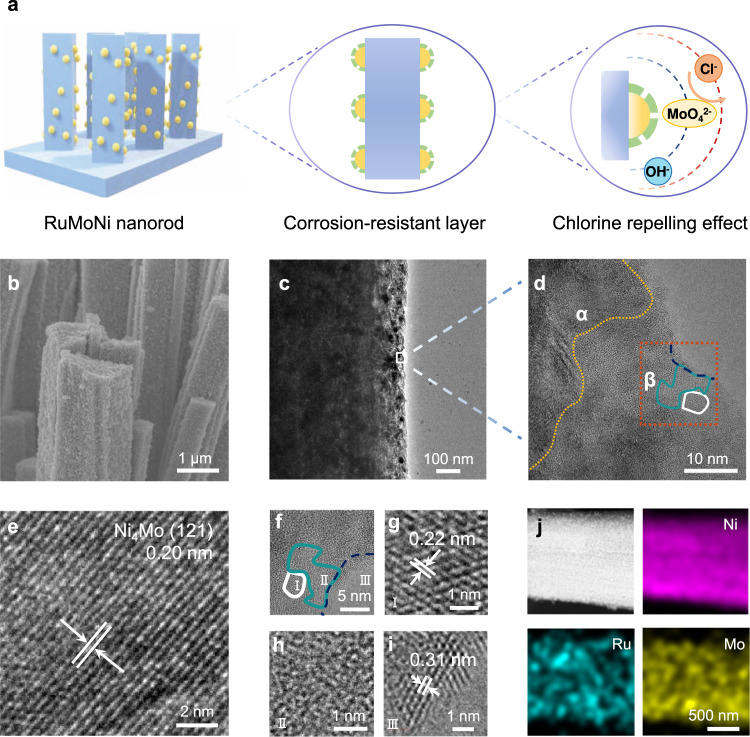
Fig. 1. Design principle and microscopic characterization of the RuMoNi electrocatalyst.
a A schematic showing the structure and corrosion-resistant strategy of the RuMoNi electrocatalyst. The light blue bar, yellow semicircle, and green dotted lines stand for nanorod-shape substrate, active sites, and corrosion-resistant layer, respectively. b SEM image of the as-prepared RuMoNi electrocatalyst. c TEM image of the RuMoNi nanorod. d HRTEM image of the RuMoNi electrocatalyst. The alpha area (α) corresponds to the region in (e), and the beta area (β) in the dashed red square corresponds to (f)–(i). e Lattice fringes of Ni4Mo (121) from the α region in (d). f The position of the three regions marked I, II, III from the β region in (d). g Lattice fringes of RuO2 (111) corresponding to region I. h HRTEM image of the reconstructed surface corresponding to region II. i Lattice fringes of NiMoO4 (220) corresponding to region III. j Energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy maps showing the uniform distribution of Ni, Ru, and Mo elements.