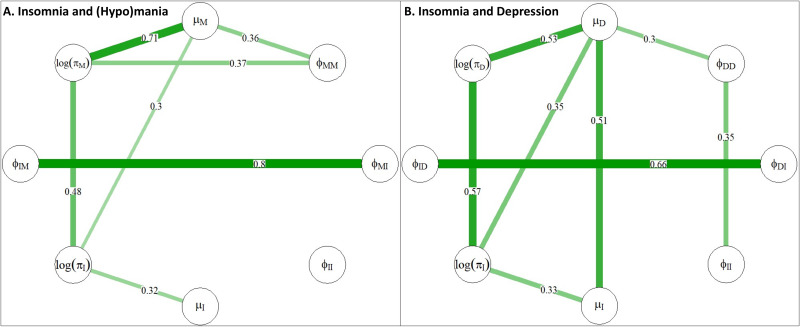
Fig. 3.
Correlations for between-person effects in bivariate models. Panel A shows bivariate correlations for between-person effects in the Insomnia-(Hypo)mania bivariate model (μM = individual mean levels of (hypo)manic symptoms, μI = individual mean levels of insomnia symptoms, log(πM) = innovation in (hypo)manic symptoms, log(πI) = innovation in insomnia symptoms, ϕMM = (hypo)mania inertia, ϕII = insomnia inertia, ϕMI = cross-lagged effect of (hypo)mania at time t regressed on insomnia at time t−1, ϕIM = cross-lagged effect of insomnia at time t regressed on (hypo)mania at time t−1). Panel B shows bivariate correlations for between-person effects in the Insomnia-Depression bivariate model (μD = individual mean levels of depression symptoms, μI = individual mean levels of insomnia symptoms, log(πD) = innovation in depression symptoms, log(πI) = innovation in insomnia symptoms, ϕDD = depression inertia, ϕII = insomnia inertia, ϕDI = cross-lagged effect of depression at time t regressed on insomnia at time t−1, ϕID = cross-lagged effect of insomnia at time t regressed on depression at time t−1). N.B. The cross-lagged parameters (ϕij) are not average individually standardised for between-person correlations.