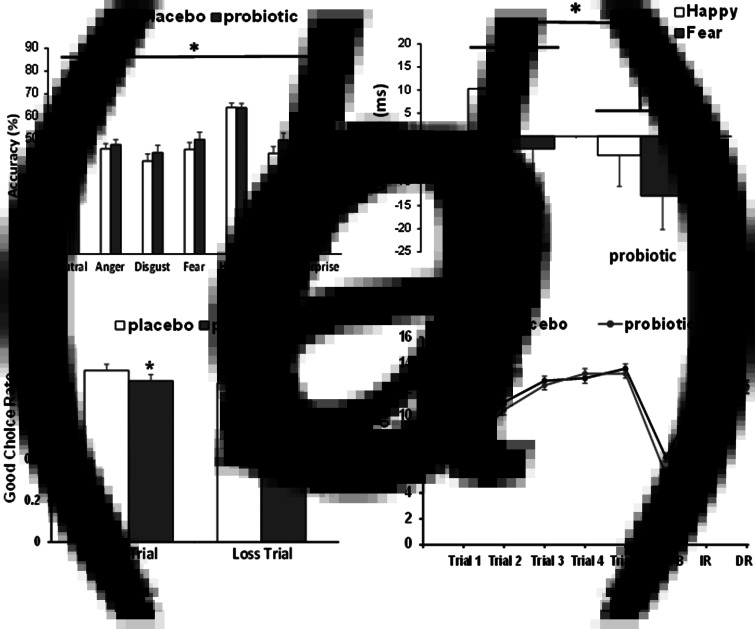
Fig. 2.
The effect of a multispecies probiotic on the performance of emotion and cognitive measures after 28 days supplementation. (a) Accuracy at identifying facial expression of all emotions was significantly greater after probiotic intake (n = 26) than placebo (n = 25). Bar indicates the effect of the group (*p < 0.05). (b) Probiotic intake reduces attentional vigilance to positive and negative emotions in the dot-probe task. In the unmasked condition, there was a main effect of group (*p < 0.05) where probiotic supplemented subjects (n = 26) displayed less attention to happy and fearful emotions compared to placebo (n = 25). (c) The influence of the placebo or probiotic on the performance of the PILT after supplementation. There was an overall effect of group (*p < 0.05), where the good choice rate for both the win and loss trials were reduced by the probiotic (n = 26) compared to placebo (n = 25). (d) AVLT learning curves after placebo or probiotic supplementation. There was a significant group × trial interaction when comparing the recollection of List B words with List A/Trial 1 words. The recall of fewer List B words by the probiotic group was indicative of proactive interference. Probiotic intake did not affect List A recall (Trials 1–5), immediate recall (IR) or delayed recall (DR). *p < 0.05, group × List B/List A -Trial 1 interaction.