Abstract
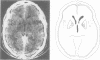
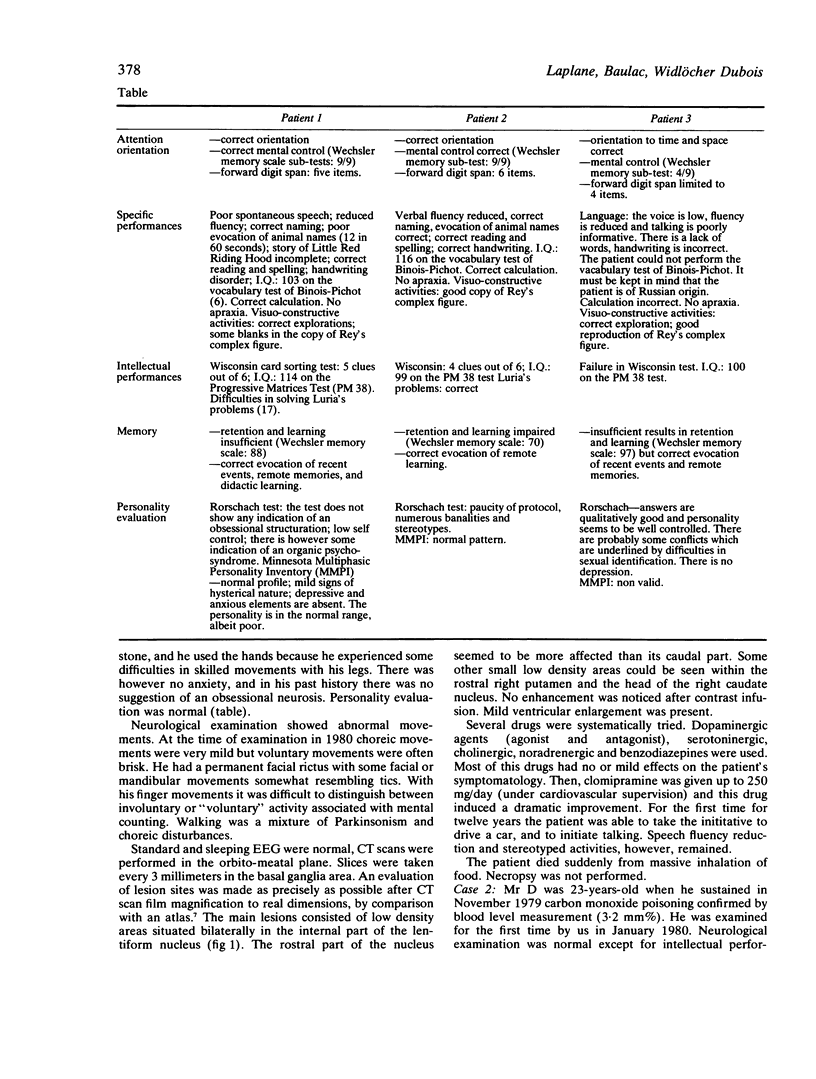
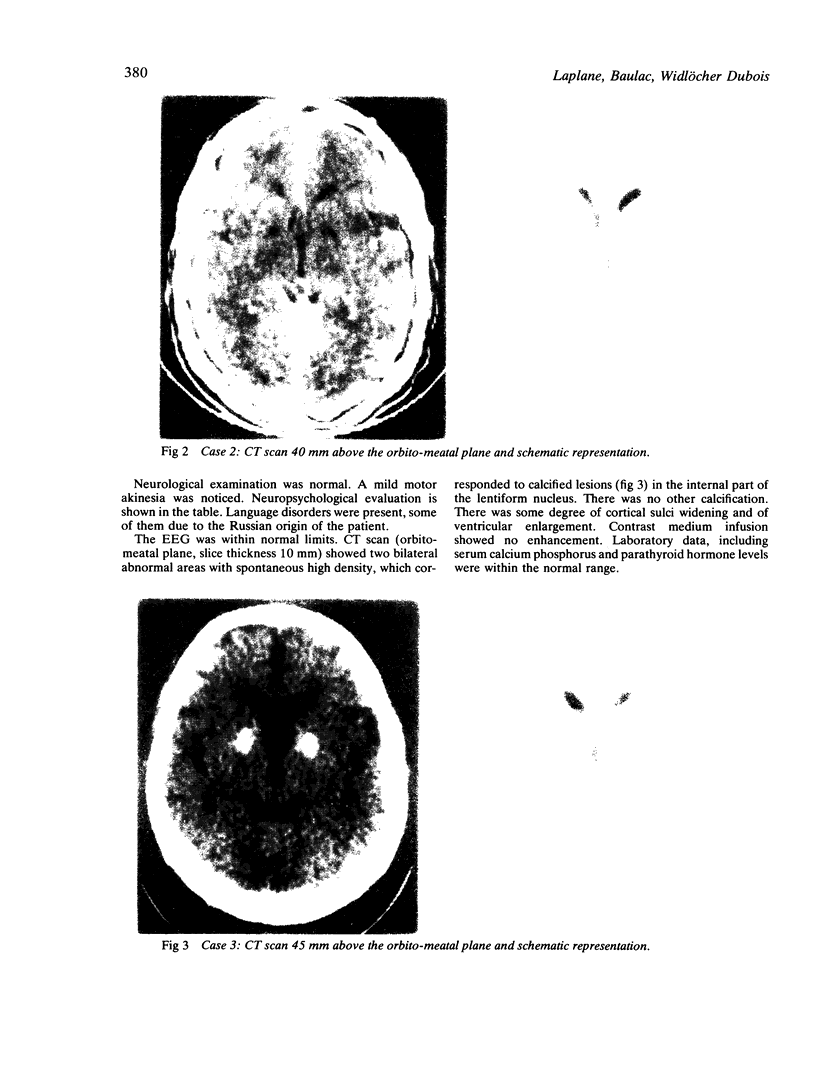
Three patients showed dramatic psychic akinesia after recovery from toxic encephalopathy. They had no or only mild motor disorders. The spontaneous psychic akinesia was reversible when the patient was stimulated, as if there was a loss of self psychic activation. Intellectual capacities were normal. Two patients had stereotyped behaviours resembling compulsions. In all patients CT cans showed bilateral lesions in the basal ganglia, mainly within the globus pallidus.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albert M. L., Feldman R. G., Willis A. L. The 'subcortical dementia' of progressive supranuclear palsy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1974 Feb;37(2):121–130. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.37.2.121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BALTHASAR K. Uber das anatomische Substrat der generalisierten Tic-Krank-heit (maladie des tics, Gilles de la Tourette): Entwicklungshemmung des corpus striatum. Arch Psychiatr Nervenkr Z Gesamte Neurol Psychiatr. 1957;195(6):531–549. doi: 10.1007/BF00343129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coyle J. T., Price D. L., DeLong M. R. Alzheimer's disease: a disorder of cortical cholinergic innervation. Science. 1983 Mar 11;219(4589):1184–1190. doi: 10.1126/science.6338589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeVito J. L., Anderson M. E. An autoradiographic study of efferent connections of the globus pallidus in Macaca mulatta. Exp Brain Res. 1982;46(1):107–117. doi: 10.1007/BF00238104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Divac I., Diemer N. H. Prefrontal system in the rat visualized by means of labeled deoxyglucose--further evidence for functional heterogeneity of the neostriatum. J Comp Neurol. 1980 Mar 1;190(1):1–13. doi: 10.1002/cne.901900102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fibiger H. C. The organization and some projections of cholinergic neurons of the mammalian forebrain. Brain Res. 1982 Nov;257(3):327–388. doi: 10.1016/0165-0173(82)90011-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GILLINGHAM F. J., KALYANARAMAN S., DONALDSON A. A. BILATERAL STEREOTAXIC LESIONS IN THE MANAGEMENT OF PARKINSONISM AND THE DYSKINESIAS. Br Med J. 1964 Sep 12;2(5410):656–659. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5410.656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman P. S., Nauta W. J. An intricately patterned prefronto-caudate projection in the rhesus monkey. J Comp Neurol. 1977 Feb 1;72(3):369–386. doi: 10.1002/cne.901710305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIRANO A., ZIMMERMAN H. M. Alzheimer's neurofibrillary changes. A topographic study. Arch Neurol. 1962 Sep;7:227–242. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1962.04210030065009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hassler R. Brain mechanisms of intention and attention with introductory remarks on other volitional processes. Prog Brain Res. 1980;54:585–614. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(08)61680-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Illum F. Calcification of the basal ganglia following carbon monoxide poisoning. Neuroradiology. 1980;19(4):213–214. doi: 10.1007/BF00376710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRAYENBUHL H., WYSS O. A., YASARGIL M. G. Bilateral thalamotomy and pallidotomy as treatment for bilateral Parkinsonism. J Neurosurg. 1961 Jul;18:429–444. doi: 10.3171/jns.1961.18.4.0429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley A. E., Domesick V. B., Nauta W. J. The amygdalostriatal projection in the rat--an anatomical study by anterograde and retrograde tracing methods. Neuroscience. 1982 Mar;7(3):615–630. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(82)90067-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley A. E., Domesick V. B. The distribution of the projection from the hippocampal formation to the nucleus accumbens in the rat: an anterograde- and retrograde-horseradish peroxidase study. Neuroscience. 1982 Oct;7(10):2321–2335. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(82)90198-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp J. M., Powell T. P. The cortico-striate projection in the monkey. Brain. 1970;93(3):525–546. doi: 10.1093/brain/93.3.525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kievit J., Kuypers H. G. Basal forebrain and hypothalamic connection to frontal and parietal cortex in the Rhesus monkey. Science. 1975 Feb 21;187(4177):660–662. doi: 10.1126/science.1114317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim R., Nakano K., Jayaraman A., Carpenter M. B. Projections of the globus pallidus and adjacent structures: an autoradiographic study in the monkey. J Comp Neurol. 1976 Oct 1;169(3):263–290. doi: 10.1002/cne.901690302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klawans H. L., Stein R. W., Tanner C. M., Goetz C. G. A pure parkinsonian syndrome following acute carbon monoxide intoxication. Arch Neurol. 1982 May;39(5):302–304. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1982.00510170044012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo J. S., Carpenter M. B. Organization of pallidothalamic projections in the rhesus monkey. J Comp Neurol. 1973 Oct 1;151(3):201–236. doi: 10.1002/cne.901510302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laplane D., Baulac M., Pillon B., Panayotopoulou-Achimastos I. Perte de l'auto-activation psychique. Activité compulsive d'allure obsessionnelle. Lésion lenticulaire bilatérale. Rev Neurol (Paris) 1982;138(2):137–141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laplane D., Widlocher D., Pillon B., Baulac M., Binoux F. Comportement compulsif d'allure obsessionnelle par nécrose circonscrite bilatérale pallido-striatale. Encéphalopathie par piqûre de guêpe. Rev Neurol (Paris) 1981;137(4):269–276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapresle J., Fardeau M. The central nervous system and carbon monoxide poisoning. II. Anatomical study of brain lesions following intoxication with carbon monixide (22 cases). Prog Brain Res. 1967;24:31–74. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6123(08)60181-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- METTLER F. A. The experimental anatomophysiologic approach to the study of diseases of the basal ganglia. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1955 Apr;14(2):115–141. doi: 10.1097/00005072-195504000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsden C. D. The mysterious motor function of the basal ganglia: the Robert Wartenberg Lecture. Neurology. 1982 May;32(5):514–539. doi: 10.1212/wnl.32.5.514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin J. P. The globus pallidus in post-encephalitic parkinsonism. J Neurol Sci. 1965 Jul-Aug;2(4):344–365. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(65)90018-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayeux R., Stern Y., Rosen J., Leventhal J. Depression, intellectual impairment, and Parkinson disease. Neurology. 1981 Jun;31(6):645–650. doi: 10.1212/wnl.31.6.645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mindham R. H. Psychiatric symptoms in Parkinsonism. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1970 Apr;33(2):188–191. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.33.2.188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortimer J. A., Pirozzolo F. J., Hansch E. C., Webster D. D. Relationship of motor symptoms to intellectual deficits in Parkinson disease. Neurology. 1982 Feb;32(2):133–137. doi: 10.1212/wnl.32.2.133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nardizzi L. R. Computerized tomographic correlate of carbon monoxide poisoning. Arch Neurol. 1979 Jan;36(1):38–39. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1979.00500370068016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nauta W. J., Mehler W. R. Projections of the lentiform nucleus in the monkey. Brain Res. 1966 Jan;1(1):3–42. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(66)90103-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nobin A., Björklund A. Topography of the monoamine neuron systems in the human brain as revealed in fetuses. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1973;388:1–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parent A., De Bellefeuille L. Organization of efferent projections from the internal segment of globus pallidus in primate as revealed by fluorescence retrograde labeling method. Brain Res. 1982 Aug 12;245(2):201–213. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)90802-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parent A. Identification of the pallidal and peripallidal cells projecting to the habenula in monkey. Neurosci Lett. 1979 Dec;15(2-3):159–164. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(79)96106-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosvold H. E. The frontal lobe system: cortical-subcortical interrelationships. Acta Neurobiol Exp (Wars) 1972;32(2):439–460. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHWAB R. S., FABING H. D., PRICHARD J. S. Psychiatric symptoms and syndromes in Parkinson's disease. Am J Psychiatry. 1951 Jun;107(12):901–907. doi: 10.1176/ajp.107.12.901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEELE J. C., RICHARDSON J. C., OLSZEWSKI J. PROGRESSIVE SUPRANUCLEAR PALSY. A HETEROGENEOUS DEGENERATION INVOLVING THE BRAIN STEM, BASAL GANGLIA AND CEREBELLUM WITH VERTICAL GAZE AND PSEUDOBULBAR PALSY, NUCHAL DYSTONIA AND DEMENTIA. Arch Neurol. 1964 Apr;10:333–359. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1964.00460160003001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawa G. M., Watson C. P., Terbrugge K., Chiu M. Delayed encephalopathy following carbon monoxide intoxication. Can J Neurol Sci. 1981 Feb;8(1):77–79. doi: 10.1017/s031716710004289x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selby G. Stereotactic surgery for the relief of Parkinson's disease. 1. A critical review. J Neurol Sci. 1967 Sep-Oct;5(2):315–342. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(67)90139-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Switzer R. C., 3rd, Hill J., Heimer L. The globus pallidus and its rostroventral extension into the olfactory tubercle of the rat: a cyto- and chemoarchitectural study. Neuroscience. 1982;7(8):1891–1904. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(82)90005-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeterian E. H., Van Hoesen G. W. Cortico-striate projections in the rhesus monkey: the organization of certain cortico-caudate connections. Brain Res. 1978 Jan 6;139(1):43–63. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90059-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Kooy D., Carter D. A. The organization of the efferent projections and striatal afferents of the entopeduncular nucleus and adjacent areas in the rat. Brain Res. 1981 Apr 27;211(1):15–36. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90064-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]