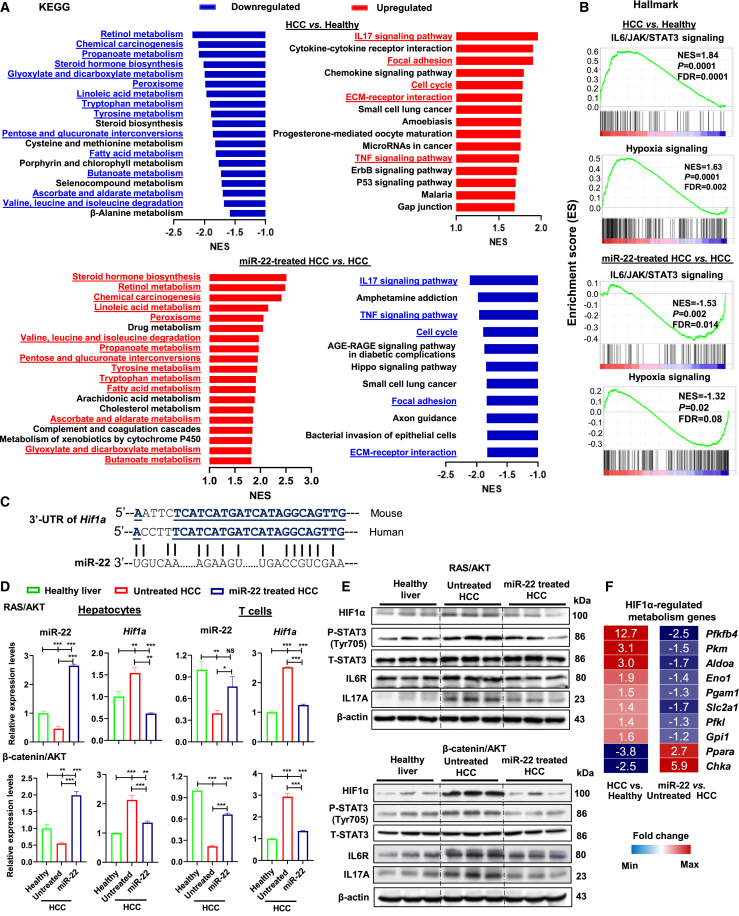
Figure 2.
miR-22 treatment restores metabolic programs and reduces inflammatory signaling accompanied by reduced HIF1α expression in the liver, hepatocytes, and T cells
(A) Pathways enriched due to HCC formation or miR-22 treatment revealed by GSEA based on KEGG gene sets. miR-22-reversed pathways are underlined and highlighted in red (upregulated) or blue (downregulated). NES, normalized enrichment score. (B) Enriched IL6/JAK/STAT3 and hypoxia signaling by comparing HCC vs. healthy livers or miR-22 treated vs. untreated HCC as demonstrated by GSEA based on hallmark gene sets. (C) Human and mouse miR-22 have conserved sequences, which partially pair with the 3′ UTR of the human and mouse Hif1a gene. (D) The level of miR-22 and HIF1α in hepatocytes and T cells isolated from livers of healthy, HCC, and miR-22-treated HCC mice (n = 3). (E) The levels of indicated proteins in the HIF1α/IL6/STAT3/IL17 axis were determined by western blot (n = 3). (F) The fold changes of HIF1α-regulated metabolism-related genes are shown in the heatmap based on RNA-seq data. Data represent mean ± SD. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001 by one-way ANOVA (D).