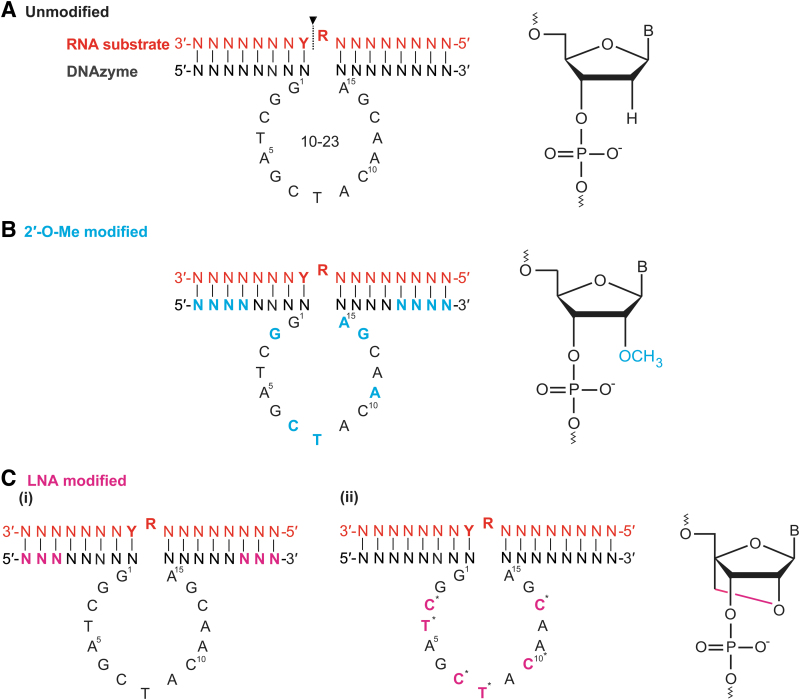
FIG. 2.
Modified and unmodified 10–23 DNAzymes. A/C/G/T = specific nucleotides, R = purine, Y = pyrimidine, N = any nucleotide, B = any nucleotide base, P = phosphate, O = oxygen and C = carbon. Nucleotide color denotes chemistry: red = RNA, black = DNA, blue = 2′-O-Me, and pink = LNA. (A) Unmodified DNAzyme. The DNAzyme binds an RNA substrate and cleaves it primarily between a purine (R) and a pyrimidine (Y) (cleavage site indicated by arrow). (B) A widely used 2′-O-Me modification scheme, with four or five 2′-O-Me modifications at the 3′ and 5′ ends and six modifications in the core at positions G2, C7, T8, A11, G14, A15. (C) Common LNA modifications are at either (i) the first and last three nucleotides of the arms, or (ii) individual nucleotides of the core. As denoted by the asterisks, only one of these indicated nucleotides is LNA chemistry in any DNAzyme of this design. Adapted from Ref. Santoro and Joyce [21]. 2′-O-Me, 2′-O-methyl; LNA, locked nucleic acid.