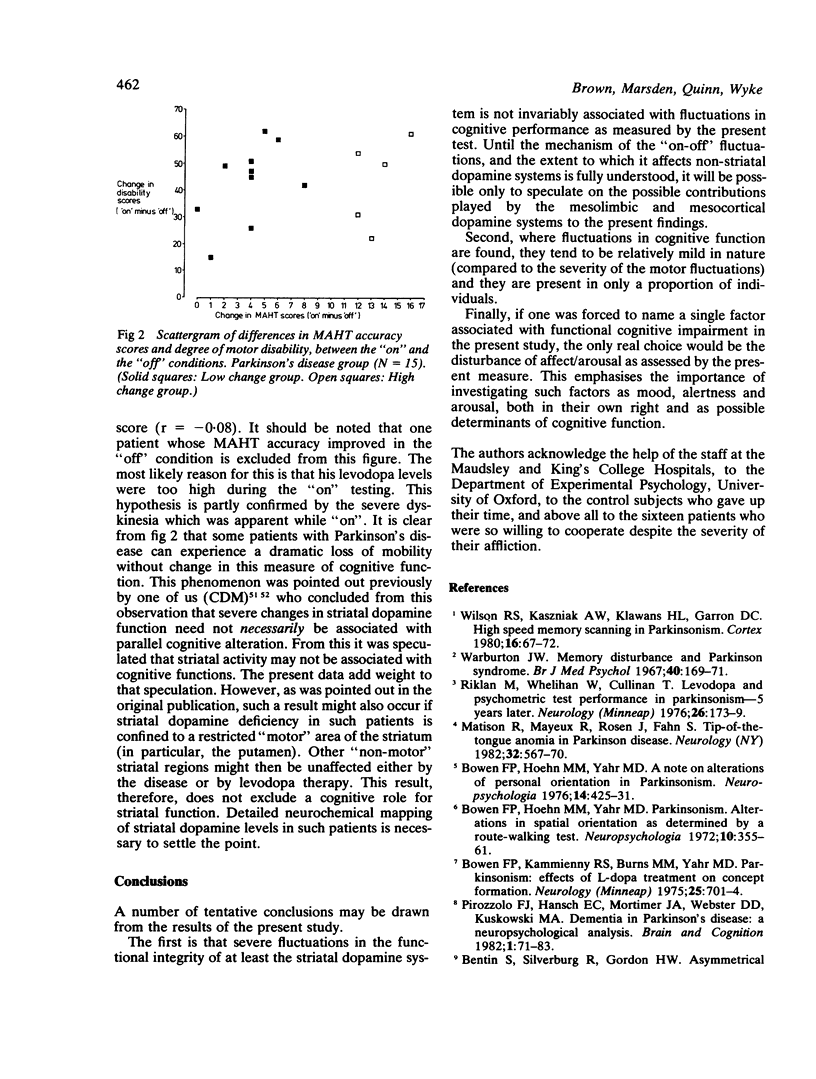
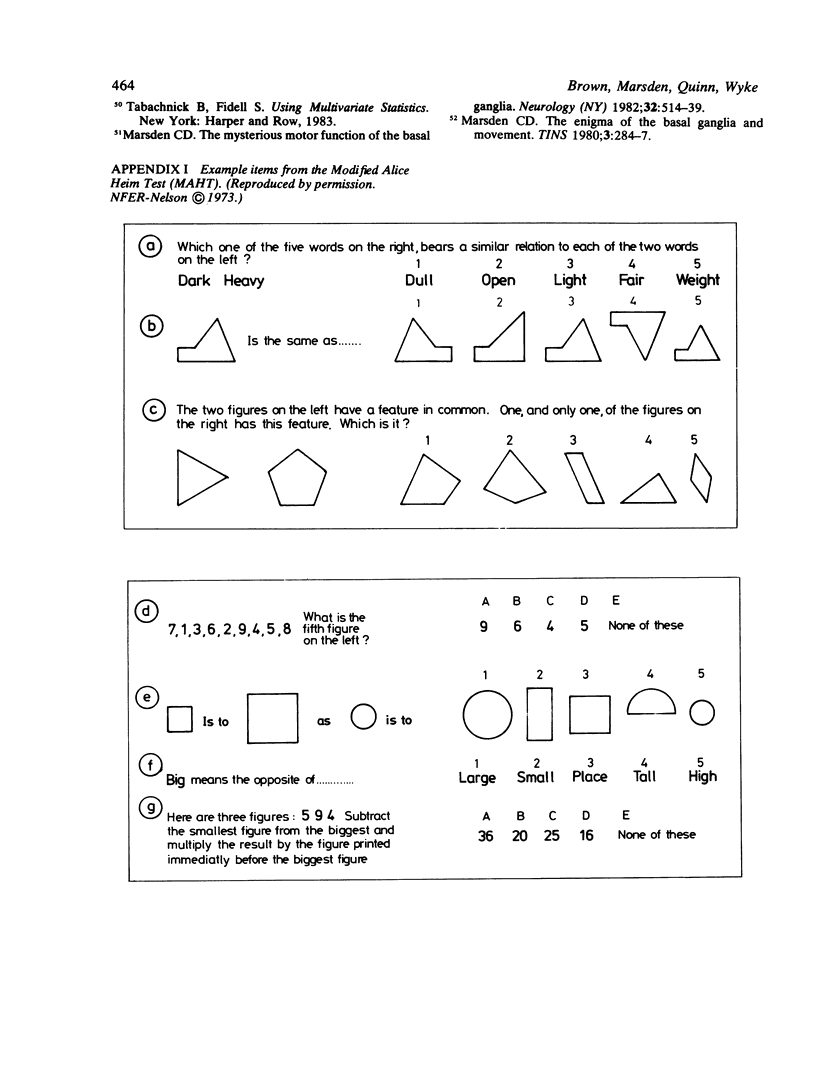
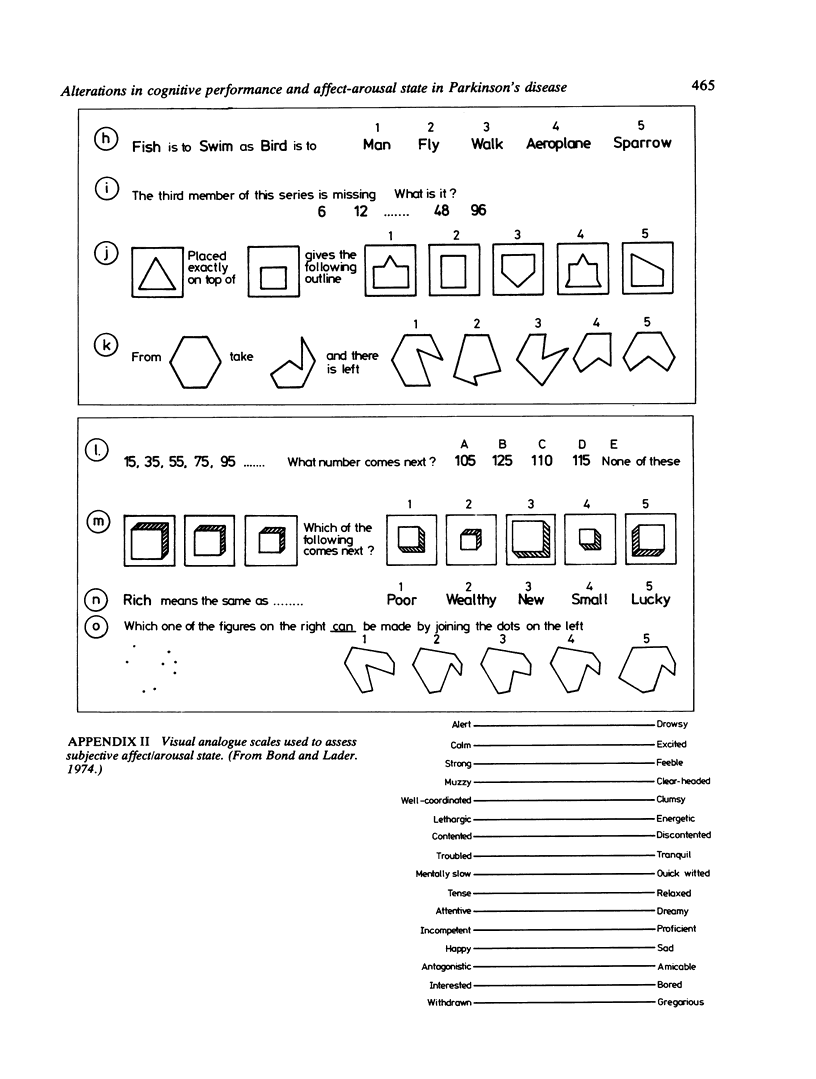
Abstract
Sixteen patients with idiopathic Parkinson's disease were selected who were all showing severe fluctuations in motor function ("on-off" phenomenon). Measures of cognitive function and of subjective affect/arousal state were taken on two occasions, once when "on" and once when "off". Twenty-five matched normal controls were also assessed on the same measures. Results revealed, on the average, a drop in cognitive function plus an adverse swing in affect/arousal state, in the patient group in the "off" condition, compared to the levels when "on". Analysis of the data suggested that the main factor associated with cognitive function when "off" was not the severity of disability but the level of affect/arousal. The fluctuations in cognitive function found tended to be mild relative to the severe changes in motor ability, and were present in only a proportion of patients.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alvord E. C., Jr, Forno L. S., Kusske J. A., Kauffman R. J., Rhodes J. S., Goetowski C. R. The pathology of Parkinsonism: a comparison of degenerations in cerebral cortex and brainstem. Adv Neurol. 1974;5:175–193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentin S., Silverberg R., Gordon H. W. Asymmetrical cognitive deterioration in demented and Parkinson patients. Cortex. 1981 Dec;17(4):533–543. doi: 10.1016/s0010-9452(81)80060-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernheimer H., Birkmayer W., Hornykiewicz O., Jellinger K., Seitelberger F. Brain dopamine and the syndromes of Parkinson and Huntington. Clinical, morphological and neurochemical correlations. J Neurol Sci. 1973 Dec;20(4):415–455. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(73)90175-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boller F., Mizutani T., Roessmann U., Gambetti P. Parkinson disease, dementia, and Alzheimer disease: clinicopathological correlations. Ann Neurol. 1980 Apr;7(4):329–335. doi: 10.1002/ana.410070408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowen F. P., Burns M. M., Brady E. M., Yahr M. D. A note of alterations of personal orientation in Parkinsonism. Neuropsychologia. 1976;14(4):425–429. doi: 10.1016/0028-3932(76)90071-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowen F. P., Hoehn M. M., Yahr M. D. Parkinsonism: alterations in spatial orientation as determined by a route-walking test. Neuropsychologia. 1972 Sep;10(3):355–361. doi: 10.1016/0028-3932(72)90027-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowen F. P., Kamienny R. S., Burns M. M., Yahr M. Parkinsonism: effects of levodopa treatment on concept formation. Neurology. 1975 Aug;25(8):701–704. doi: 10.1212/wnl.25.8.701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown G. L., Wilson W. P. Parkinsonism and depression. South Med J. 1972 May;65(5):540–545. doi: 10.1097/00007611-197205000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celesia G. G., Wanamaker W. M. Psychiatric disturbances in Parkinson's disease. Dis Nerv Syst. 1972 Sep;33(9):577–583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotzias G. C., Papavasiliou P. S., Gellene R. Modification of Parkinsonism--chronic treatment with L-dopa. N Engl J Med. 1969 Feb 13;280(7):337–345. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196902132800701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danta G., Hilton R. C. Judgment of the visual vertical and horizontal in patients with Parkinsonism. Neurology. 1975 Jan;25(1):43–47. doi: 10.1212/wnl.25.1.43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garron D. C., Klawans H. L., Jr, Narin F. Intellectual functioning of persons with idiopathic Parkinsonism. J Nerv Ment Dis. 1972 Jun;154(6):445–452. doi: 10.1097/00005053-197206000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hakim A. M., Mathieson G. Dementia in Parkinson disease: a neuropathologic study. Neurology. 1979 Sep;29(9 Pt 1):1209–1214. doi: 10.1212/wnl.29.9_part_1.1209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henke H., Lang W. Cholinergic enzymes in neocortex, hippocampus and basal forebrain of non-neurological and senile dementia of Alzheimer-type patients. Brain Res. 1983 May 16;267(2):281–291. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)90880-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn S. Some psychological factors in Parkinsonism. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1974 Jan;37(1):27–31. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.37.1.27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Javoy-Agid F., Agid Y. Is the mesocortical dopaminergic system involved in Parkinson disease? Neurology. 1980 Dec;30(12):1326–1330. doi: 10.1212/wnl.30.12.1326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins R. B., Groh R. H. Mental symptoms in Parkinsonian patients treated with L-dopa. Lancet. 1970 Jul 25;2(7665):177–179. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)92535-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay D. W., Bergmann K. Physical disability and mental health in old age. A follow-up of a random sample of elderly people seen at home. J Psychosom Res. 1966 Jul;10(1):3–12. doi: 10.1016/0022-3999(66)90128-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavy S., Melamed E., Cooper G., Bentin S., Rinot Y. Regional cerebral blood flow in patients with Parkinson's disease. Arch Neurol. 1979 Jun;36(6):344–348. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1979.00500420054005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman A., Dziatolowski M., Kupersmith M., Serby M., Goodgold A., Korein J., Goldstein M. Dementia in Parkinson Disease. Ann Neurol. 1979 Oct;6(4):355–359. doi: 10.1002/ana.410060409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann D. M., Yates P. O. Pathological basis for neurotransmitter changes in Parkinson's disease. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 1983 Jan-Feb;9(1):3–19. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2990.1983.tb00320.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marttila R. J., Rinne U. K. Dementia in Parkinson's disease. Acta Neurol Scand. 1976 Nov;54(5):431–441. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1976.tb04375.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matison R., Mayeux R., Rosen J., Fahn S. "Tip-of-the-tongue" phenomenon in Parkinson disease. Neurology. 1982 May;32(5):567–570. doi: 10.1212/wnl.32.5.567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayeux R., Stern Y., Rosen J., Leventhal J. Depression, intellectual impairment, and Parkinson disease. Neurology. 1981 Jun;31(6):645–650. doi: 10.1212/wnl.31.6.645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meier M. J., Martin W. E. Intellectual changes associated with levodopa therapy. JAMA. 1970 Jul 20;213(3):465–466. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore R. Y., Bhatnagar R. K., Heller A. Anatomical and chemical studies of a nigro-neostriatal projection in the cat. Brain Res. 1971 Jul 9;30(1):119–135. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(71)90009-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortimer J. A., Pirozzolo F. J., Hansch E. C., Webster D. D. Relationship of motor symptoms to intellectual deficits in Parkinson disease. Neurology. 1982 Feb;32(2):133–137. doi: 10.1212/wnl.32.2.133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pirozzolo F. J., Hansch E. C., Mortimer J. A., Webster D. D., Kuskowski M. A. Dementia in Parkinson disease: a neuropsychological analysis. Brain Cogn. 1982 Jan;1(1):71–83. doi: 10.1016/0278-2626(82)90007-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell G. E. The relationship between intelligence and verbal and spatial memory. J Clin Psychol. 1979 Apr;35(2):335–340. doi: 10.1002/1097-4679(197904)35:2<335::aid-jclp2270350223>3.0.co;2-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price K. S., Farley I. J., Hornykiewicz O. Neurochemistry of Parkinson's disease: relation between striatal and limbic dopamine. Adv Biochem Psychopharmacol. 1978;19:293–300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riklan M., Whelihan W., Cullinan T. Levodopa and psychometric test performance in parkinsonism-5 years later. Neurology. 1976 Feb;26(2):173–179. doi: 10.1212/wnl.26.2.173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider E., Fischer P. A., Jacobi P., Becker H., Hacker H. The significance of cerebral atrophy for the symptomatology of Parkinson's disease. J Neurol Sci. 1979 Jul;42(2):187–197. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(79)90050-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selby G. Cerebral atrophy in Parkinsonism. J Neurol Sci. 1968 May-Jun;6(3):517–559. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(68)90034-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thierry A. M., Tassin J. P., Blanc G., Glowinski J. Studies on mesocortical dopamine systems. Adv Biochem Psychopharmacol. 1978;19:205–216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warburton J. W. Memory disturbance and the Parkinson syndrome. Br J Med Psychol. 1967 Jun;40(2):169–171. doi: 10.1111/j.2044-8341.1967.tb00566.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitehouse P. J., Hedreen J. C., White C. L., 3rd, Price D. L. Basal forebrain neurons in the dementia of Parkinson disease. Ann Neurol. 1983 Mar;13(3):243–248. doi: 10.1002/ana.410130304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitehouse P. J., Price D. L., Clark A. W., Coyle J. T., DeLong M. R. Alzheimer disease: evidence for selective loss of cholinergic neurons in the nucleus basalis. Ann Neurol. 1981 Aug;10(2):122–126. doi: 10.1002/ana.410100203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson R. S., Kaszniak A. W., Klawans H. L., Garron D. C. High speed memory scanning in parkinsonism. Cortex. 1980 Mar;16(1):67–72. doi: 10.1016/s0010-9452(80)80022-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wycis H. T., Cunningham W., Kellett G., Spiegel E. A. L-dopa in the treatment of post-surgical Parkinson patients. J Neurosurg. 1970 Mar;32(3):281–285. doi: 10.3171/jns.1970.32.3.0281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


