Figure 2.
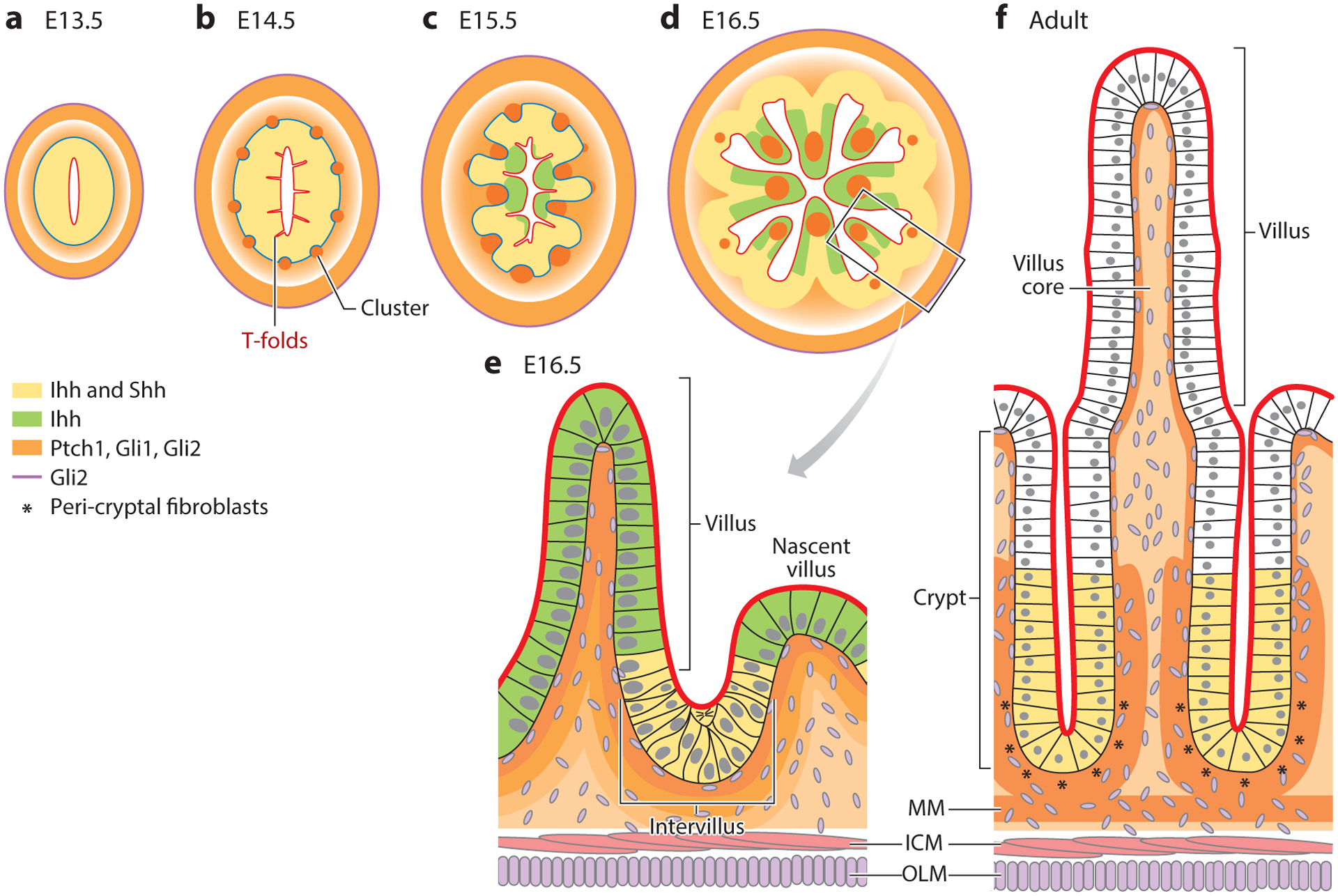
Dynamic expression of Hh pathway components during intestinal development and adult homeostasis. Expression patterns in the mouse are summarized from References 1, 2, 6, 10, and 108 and color coded as indicated. Prior to villus formation, Shh and Ihh are expressed by all epithelial cells (a,b). As villi emerge (c–e), cells above the mesenchymal clusters cease to express Shh, while Ihh expression remains in all epithelial cells, though at lower levels. In adult intestine, Shh and Ihh expression is restricted to crypts (f). Hh signals are received by multiple cell types in the mesenchyme. At E13.5, the Hh receptor, Ptch1, as well as Gli1 and Gli2 transcription factors, are expressed in a gradient with highest expression in mesenchymal cells closest to the epithelial source of Hh ligand and in the ICM. As development proceeds, all three proteins are highly expressed in mesenchymal clusters, villus cores, subepithelial fibroblasts, peri-cryptal fibroblasts (* in panel f), and the MM. Gli2, but not Ptch1 and Gli1, is expressed in the OLM and in many cells of the mesenchyme (all stages). Serosal cells (not shown) also express Gli2, and some express Gli1. Abbreviations: E, embryonic day; Hh, Hedgehog; ICM, inner circular muscle; Ihh, Indian Hedgehog; MM, muscularis mucosa; OLM, outer longitudinal muscle; Shh, Sonic Hedgehog.
