Figure 5. Examples of logic-gating strategies tested in CAR T cells.
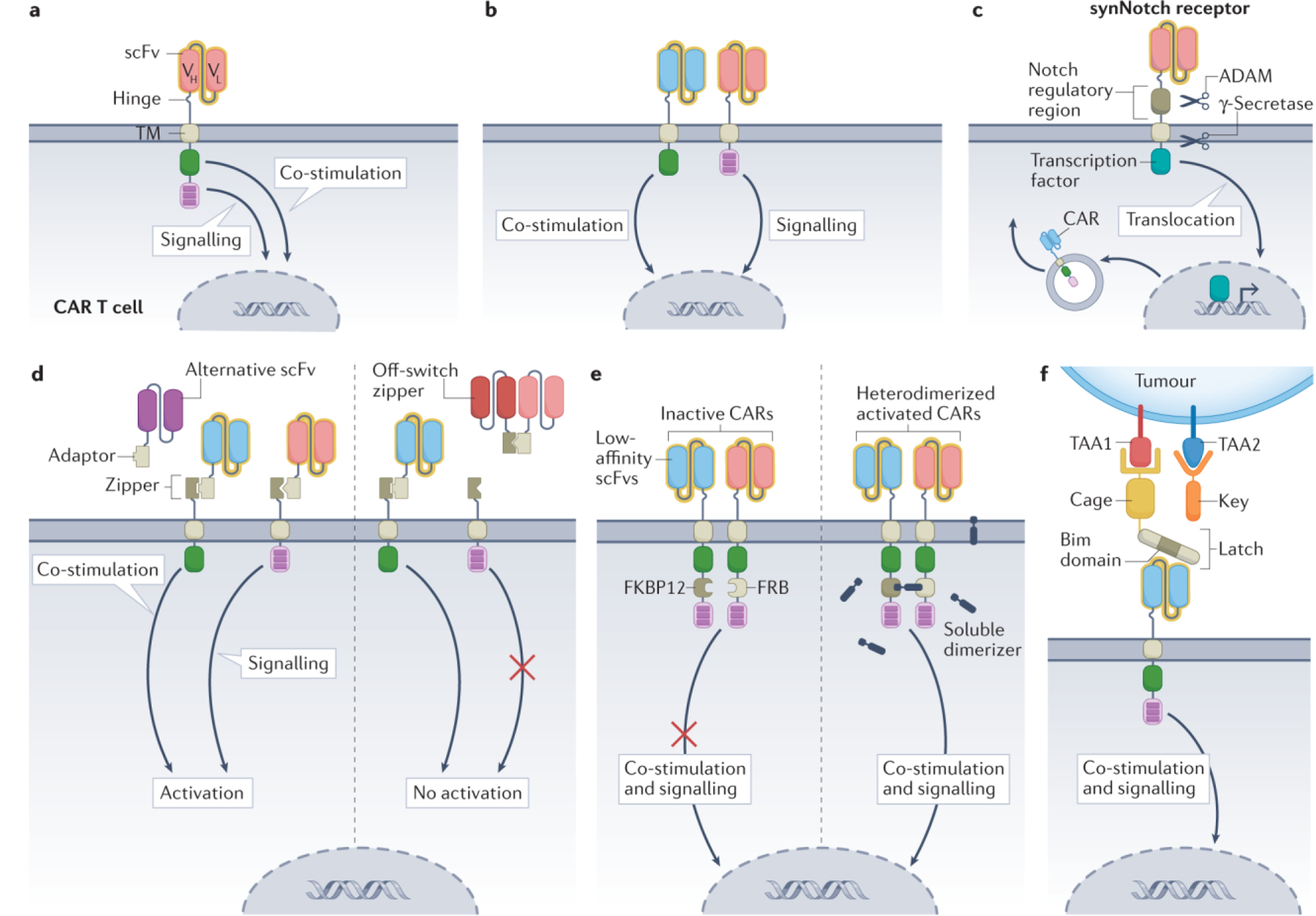
a, Conventional second-generation chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells combine the two signals required for optimal CAR T cell function within a single construct. b, Dual AND-logic CAR T cells accomplish signalling and co-stimulation via two independent receptors that bind distinct tumour-associated antigens (TAAs)84. c, Synthetic Notch (synNotch) CAR T cells constitutively express a synNotch receptor. Antigen binding by this receptor leads to exposure of protein cleavage sites in the Notch regulatory region and transmembrane domains, allowing sequential cleavage via the enzymes ADAM and γ-secretase. This releases a tethered, intracellular transcription factor, which promotes CAR expression. The expressed CAR can recognize its own cognate antigen and trigger a cytotoxic response97. d, Split, universal and programmable (SUPRA) CAR T cells express a leucine zipper as an extracellular binding domain. The leucine zipper can bind a leucine adaptor molecule carrying a single-chain variable fragment (scFv). This soluble adaptor–scFv endows the CAR T cells with antigen recognition capabilities toward a specific target. As the adaptor–scFv conjugate is administered independently to the CAR T cells, infusing a different scFv allows in vivo switching of the CAR target. A soluble zipper–scFv can competitively bind the adaptor–scFv, preventing CAR T cell signalling. This system can also be designed using the AND-logic split architecture as in b108. e, AND-logic avidity-controlled CAR T cells contain low-affinity scFvs that rely on avidity for TAA encounter. CAR T cell activation is dependent on antigen recognition and dimerization of two low-affinity CARs in the presence of a soluble dimerizer109. f, The Co-LOCKR system uses cage and key intermediary proteins to recognize and bind to target cells. The cage and key molecules carry a TAA binding domain, whereas only the cage carries a latch that contains a hidden Bim domain (binding site). Once the cage and key bind their cognate antigens, the latch is released, exposing the Bim domain and allowing recognition by CAR T cells119. Co-stimulation is either via CD28 or 4–1BB. TF, transcription factor; TM, transmembrane domain; VH, heavy chain variable region; VL, light chain variable region.
