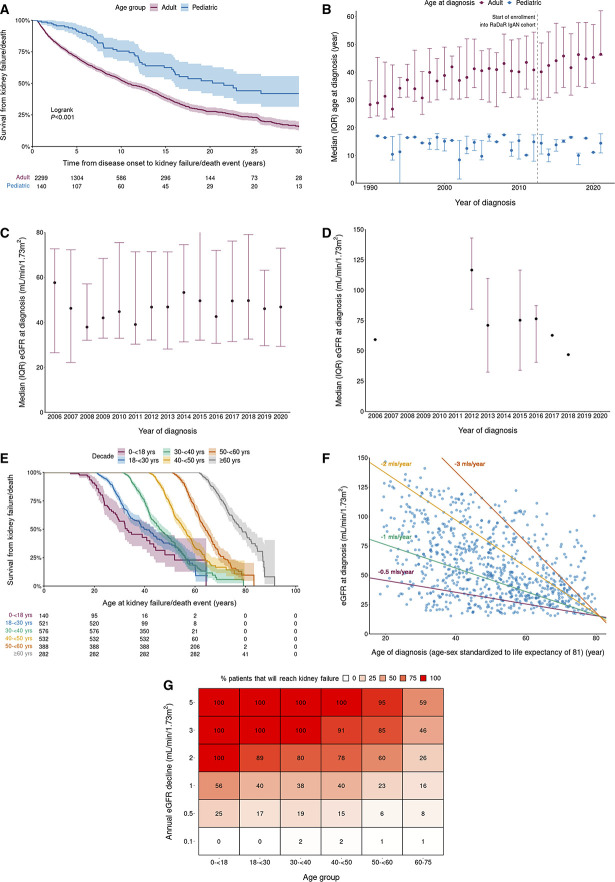
Figure 1.
Outcomes and characteristics for the full-analysis population. (A) Kaplan–Meier survival curves of time to kidney failure/death event in adult versus pediatric patients. (B) Age at diagnosis by decade in adult versus pediatric patients. Dotted line highlights first year of recruitment of patients with IgA nephropathy into RaDaR (2013). (C) eGFR at diagnosis by year in adult patients. (D) eGFR at diagnosis by year in pediatric patients. (E) Kaplan–Meier survival curves of time to kidney failure/death event on the basis of age at diagnosis. (F) Scatter plot of eGFR at diagnosis against age at diagnosis for patients with IgA nephropathy. Reference lines showing rates of decline that reach eGFR=15 by age-sex standardized life expectancy of 81 years. Patients below a reference line will reach an eGFR of 15 ml/min per 1.73 m2 before 81 years at the reference line rate of loss of eGFR. (G) Percentage of patients who will reach kidney failure during life expectancy on the basis of their eGFR at diagnosis. Life expectancy is based on year of birth and sex. IQR, interquartile range; RaDaR, UK National Registry of Rare Kidney Diseases.