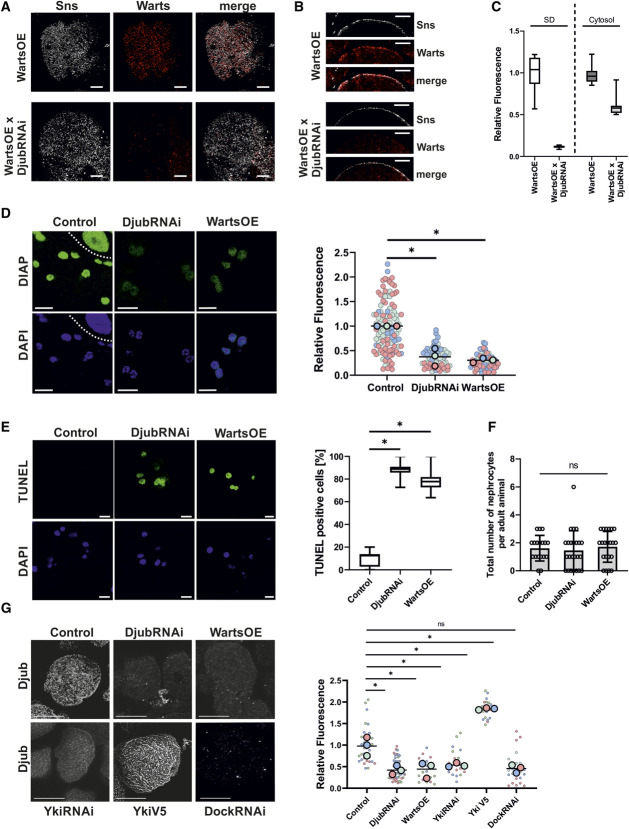
Figure 2.
Ajuba protein localization and Hippo pathway activity depend on each other. (A). Immunostaining of Sns (gray) and myc (red) in third instar larvae garland nephrocytes overexpressing myc-Warts (WartsOE) with and without additional Djub knockdown (WartsOE versus WartsOE×DjubRNAi) demonstrates decreased expression of Warts in Djub-knockdown nephrocytes. (B) Cross-section images of nephrocytes as used in (A) show reduced Warts signal at the cortex of the nephrocyte stained with Sns. (C) Densitometric quantification of myc-Warts signal on the nephrocyte surface and in the cytoplasm from nephrocytes as used in (A). Djub knockdown results in significantly reduced Warts signal on the surface, approximately 10% of the Warts signal at endogenous Djub level. Cytoplasmic Warts signal was also significantly decreased after DjubRNAi, but the level was only halved. This indicates that Djub is essential for Warts localization at SD and that a loss of SD association increases degradation of Warts. (D) Djub knockdown and WartsOE both activate the Hippo pathway, resulting in decreased transcription of the Yki target gene DIAP; the cell above the dotted line in Control is part of the stomach. Densitometric quantification of DIAP signal in the nucleus shows significantly reduced Yki activity in DjubRNAi and WartsOE nephrocytes (n>60). (E) TUNEL assays indicate apoptotic processes in DjubRNAi and Warts overexpression garland nephrocytes (>12 individual larvae per genotype). Statistical analyses show a significant increase of TUNEL-positive nephrocytes for Djub knockdown and Warts overexpression. (F) Quantification of the total nephrocyte number in adult flies (>3 days older than larvae used for other nephrocyte studies) shows no significant reduced number of nephrocyte caused by Djub knockdown or Warts overexpression, despite induction of apoptosis shown in (E). For visualization, nephrocytes were stained with WGA. (G) Immunostaining with antibody against Djub in third instar larvae garland nephrocytes. In comparison with control, the Djub signal was strongly decreased in nephrocytes with knockdown of Djub or Yki (DjubRNAi, YkiRNAi) and WartsOE. Overexpression of Yki-V5 increases Djub surface expression. Knockdown of Dock (DockRNAi) led to a similar decrease in SD-associated Djub and suggests Dock as a molecular connector between Djub and the SD protein complex. Densitometric quantification of the Djub signal on the GCN surface from mutants shown in (D) confirms significance of the changes in Djub surface expression (n>20). *P < 0.05. Scale bars (A and B) 5 µm and (D–F) 10 µm. Figure 2 can be viewed in color online at www.jasn.org.