Figure 1:
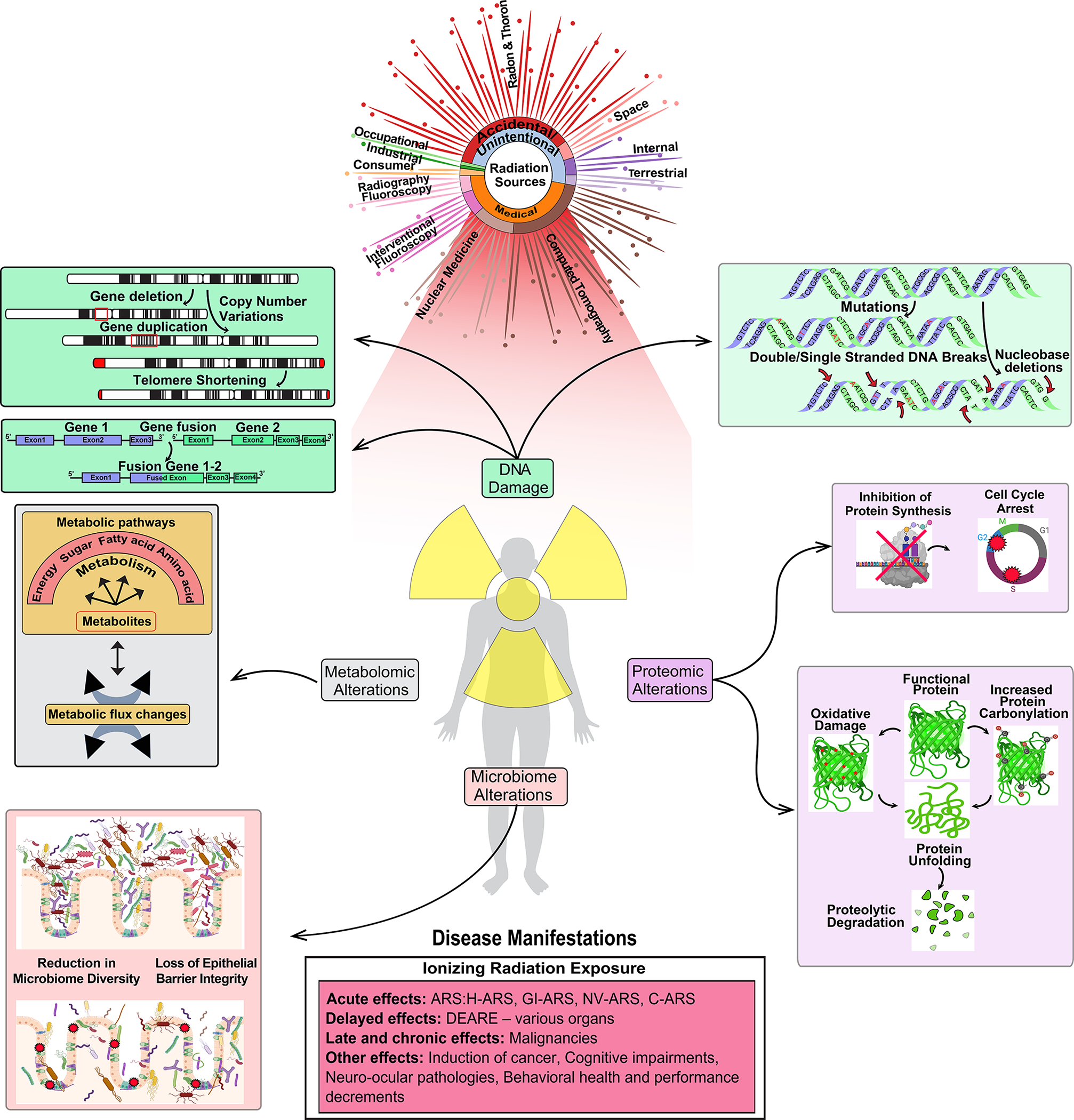
Overview of the sources of radiation exposure and their impact on human biology. The damaging effects of irradiation on DNA, proteins, metabolites/lipidomes, microbiome, and the resulting health consequence in humans are depicted. Significant sources of natural and medical IR are mentioned here. Exposure to radiation induces DNA damage, leading to chromosomal aberrations, gene fusions, DNA breaks, and mutations. Proteomic alterations can lead to inhibition of protein synthesis, changes in protein folding and degradation. Radiation exposure also affects gut health through impairment of gut epithelial barrier integrity, villus shortening, and causes reduction in microbiome diversity. Irradiation also leads to a lowered activity in key metabolic pathways including glycolysis and energy metabolism. Exposure to high dose IR causes acute, delayed, late, and chronic health effects. Only the major health consequence from both high and low dose radiation exposure is represented in this figure.
