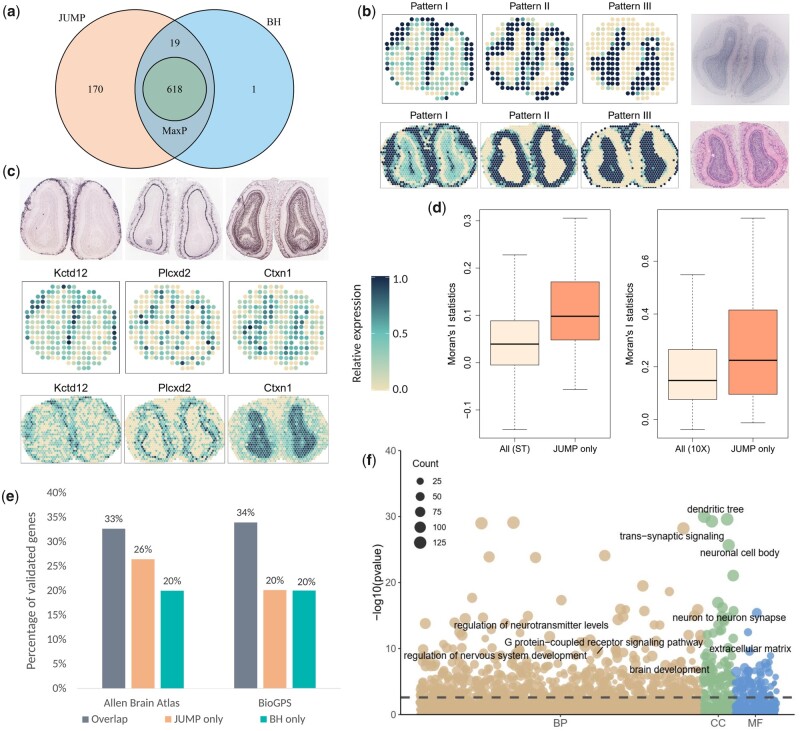
Figure 3.
Analysis and validation results of the mouse olfactory bulb data measured with ST technology and 10× Visium technology. (a) Venn diagram shows the number of replicable SVGs identified by different methods at FDR level 0.05 and the intersection of discoveries. (b) Three distinct spatial expression patterns based on the 807 replicable SVGs identified by JUMP in the ST study (top) and 10× Visium study (bottom). Each pattern summarizes the relative expression levels across spatial spots. The corresponding hematoxylin and eosin staining images for the two studies are shown in the right panel. (c) Spatial expression patterns of three representative genes identified by JUMP, corresponding to Patterns I–III, respectively. In situ hybridization images of corresponding genes obtained from the Allen Brain Atlas (atlas.brain-map.org) are shown in the top panel. (d) The box plot shows Moran’s I statistic of the 189 replicable SVGs additionally identified by JUMP and that of all genes based on the ST study (left) and the 10× Visium study (right). (e) The bar chart displays the number of replicable SVGs additionally identified by JUMP and BH compared to that identified by all three methods. They were validated in two reference gene lists from the Harmonizome database: one from the Allen Brain Atlas dataset and the other from the BioGPS dataset. (f) The bubble plot shows the GO enrichment analysis result of JUMP, including different GO term categories: BP, CC and MF. The horizontal dashed line represents the FDR level 0.01. The size of a bubble represents the counts of corresponding gene sets.