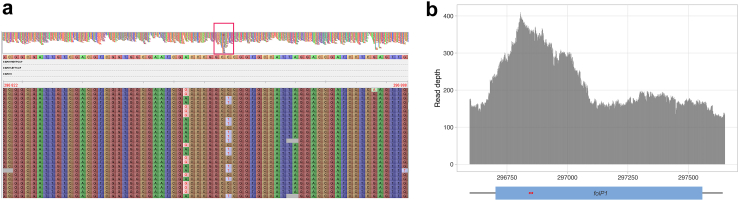
Fig. 5.
WGS reads of sample WGS23 mapped to the genome of the M. leprae TN strain, around folP1. (a) Variants detected in folP1 are carried by different reads, indicating that they originate from distinct regions. The top part of the figure shows read coverage depths at the folP1 and flanking regions. A red box indicates the folP1 region with a coverage depth up to twice as high as the depth of flanking regions. The bottom part shows a zoom-in of the folP1 region showing the aligned sequence reads. Genomic positions of the extremities of the region shown are indicated on the top right and top left. Different rows represent independent sequence reads. G and T variants are never found in combination in a read, resulting in mixed wild type/variant calls with a frequency of ∼50% of the reads, at each of both variant positions. (b) Read depth at the folP1 region, with 100bp flanking sequences. Positions of the folP1 coding sequence and the two variants detected at a frequency of ∼50% by WGS are represented by a blue rectangle and red stars, respectively. Variants are 7bp apart in the reference genome.