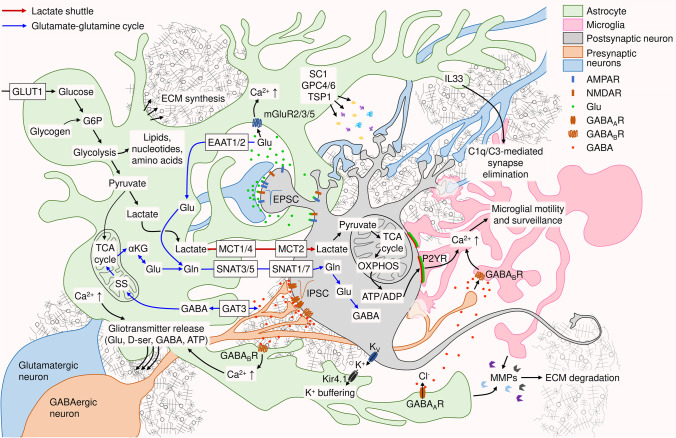
Fig. 1.
Graphical summary of neuroplasticity mechanisms mediated by glia. Intimate interactions between astrocytes, microglia, and ECM allow for dynamic control of neuronal activity and synaptic transmission. While astrocytes regulate neuronal function by providing metabolic support, modulating neurotransmission, and producing ECM, microglia can sculpt neuronal synapses in an activity-dependent manner. Abbreviations: αKG, α-ketoglutarate; ATP/ADP, adenosine tri- and diphosphate; AMPAR, AMPA receptor; D-ser, D-serine; EAAT, excitatory amino acid transporter; ECM, extracellular matrix; EPSC, excitatory postsynaptic current; IPSC, inhibitory postsynaptic current; G6P, glucose-6-phosphate; GABAAR, ionotropic GABA receptor A; GABABR, metabotropic GABA receptor B; GAT3, GABA transporter 3; Glu, glutamate; Gln, glutamine; GLUT1, glucose transporter 1; IL33, interleukin 33; mGluR, metabotropic glutamate receptor; MMPs, matrix metalloproteases; MCT, monocarboxylate transporter; NMDAR, NMDA receptor; OXPHOS, oxidative phosphorylation; P2YR, purinergic P2Y receptor; SNAT, sodium-coupled neutral amino acid transporter; SS, succinic semialdehyde; TCA cycle, tricarboxylic acid cycle (Krebs cycle)