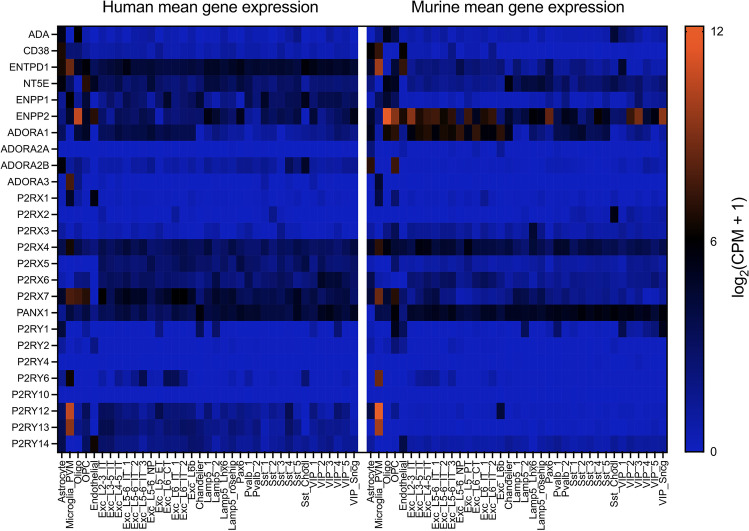
Fig. 1.
Gene expression data heatmap of 26 enzymes and receptors (y axis) involved in purinergic signaling in 37 conserved cell types (x axis) between humans (left) and mice (right). All enzymes and receptors are listed with gene names. For human single-nucleus RNA-sequencing data (SMART-SEQ) of the middle temporal gyrus (MTG), 15,928 nuclei from 8 human tissue donors were analyzed [10] (Allen Institute for Brain Science. Allen Brain Map, Cell Types Database, RNA-Seq Data. Available from: https://celltypes.brain-map.org/rnaseq/human/mtg). For the mouse cortex single-cell RNA-sequencing dataset (SMART-SEQ) 14,249 cells from the primary visual cortex (V1) and 9573 cells from the anterior lateral motor cortex (ALM) were profiled [11] (Allen Institute for Brain Science. Allen Brain Map, Cell Types Database, RNA-Seq Data. Available from: https://celltypes.brain-map.org/rnaseq/mouse/v1-alm). Expression levels were quantified as log2-transformed counts per million (CPM) of intronic plus exonic reads. Homologous cell types between the two species [10] can be divided into 5 non-neuronal cells (astrocytes, microglia and perivascular macrophages (PVM), oligodendrocytes (Oligo), oligodendrocyte precursor cells (OPC), and endothelial cells), 12 excitatory neuron (Exc) types named after the originating brain lamina (L) and their projection targets (intratelencephalic (IT), extratelencephalic-pyramidal tract (ET), near-projecting (NP), corticothalamic (CT)) and 20 inhibitory neuron cell types. Inhibitory neurons are further subdivided into lysosomal associated membrane protein family member 5 (Lamp5), somatostatin (Sst), parvalbumin (Pvalb), vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (Vip), and paired box 6 (Pax6) expressing cells and chandelier neurons