Fig. 3.
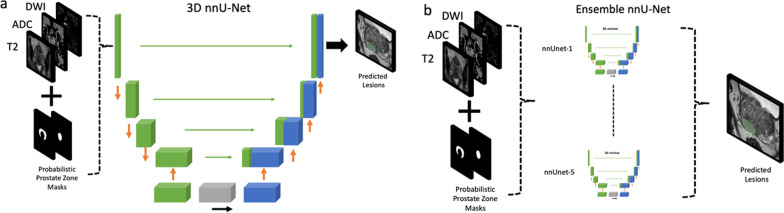
The 3D nnU-Net model for detecting clinically significant prostate cancer. a The 3D nnU-Net was fed with T2W imaging, diffusion-weighted imaging, and apparent diffusion coefficient maps along with probabilistic prostate masks via five different channels. The model was trained on the publicly available Prostate Imaging: Cancer AI training data using the significant cancer masks provided by the organizers as the ground truth. b The 3D nnU-Net model was trained using a fivefold cross-validation approach. Then, the ensemble of five nnU-Net models was used to make the final predictions