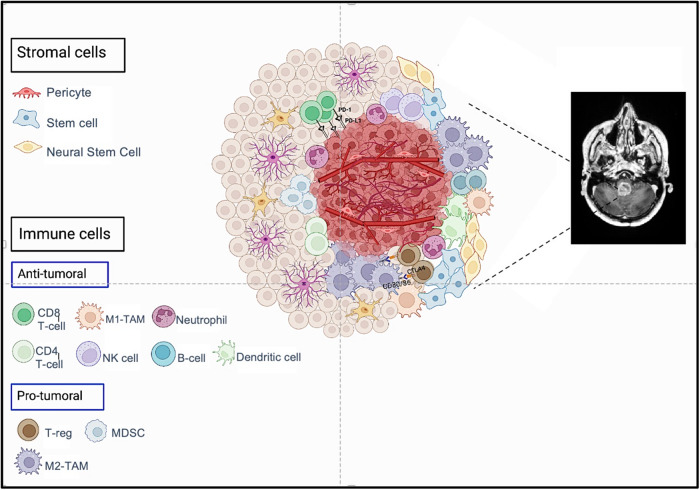
Fig. 1. Cellular composition of the glioma microenvironment (created by Biorender.com).
The glioma microenvironment is mostly composed of tumor cells, immune cells, and stromal tissue. The most prominent cells of the immune compartment include tumor-associated macrophages, regulatory T-cells, myeloid-derived suppressor cells, T lymphocytes, natural killer cells, and dendritic cells. These cells interact with other components of the tumor microenvironment and play a role in regulating immune response, either through their pro- or anti-tumoral function, subsequently affecting tumor development, progression, and response to therapy. TAMs tumor-associated macrophages, T-reg regulatory T-cells, MDSCs myeloid-derived suppressor cells, NK cell natural killer cell.