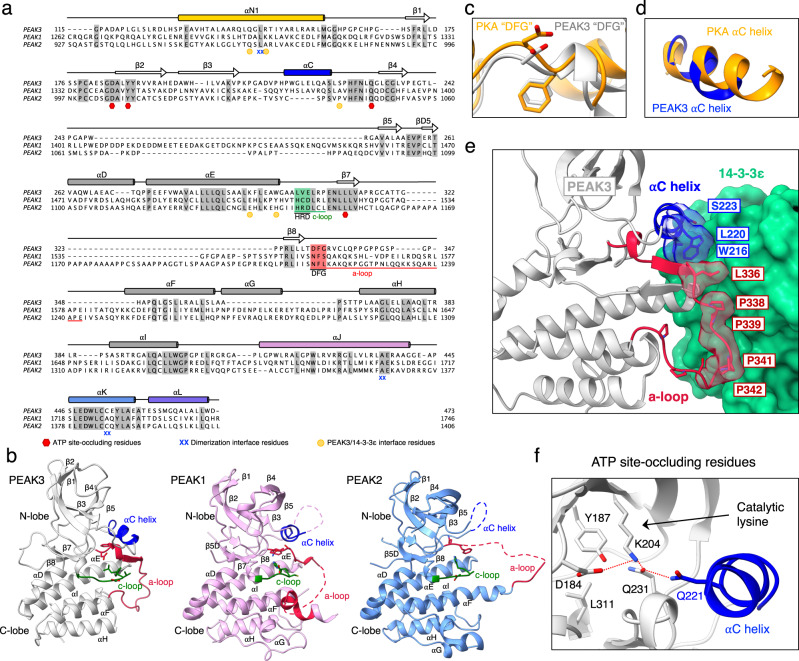
Fig. 4. Unique features of the PEAK3 pseudokinase domain.
a Protein sequence alignment of PEAK1, PEAK2, and PEAK3 depicting secondary structure elements, sequence motifs corresponding to canonical catalytic motifs in active kinases, and key dimerization interface residues based on structures of PEAK1 (PDB ID: 6BHC), PEAK2 (PDB ID: 5VE6) and PEAK3 (PEAK3/14-3-3 complex). Conserved residues are shaded in gray, αC helix is shown in blue while catalytic and activation loops with their corresponding motifs are highlighted in green and red, respectively. Residues involved in PEAK3 dimerization and those shown to occlude the pseudoactive site and PEAK3/14-3-3 secondary interface residues are marked by the indicated symbols. b Comparison of PEAK3 pseudokinase domain (light gray) with PEAK1 (light pink, PDB ID: 6BHC) and PEAK2 (light blue, PDB ID: 5VE6) pseudokinase domains with key structural elements highlighted (catalytic loop [c-loop] in green, activation loop [a-loop] in red, αC helix in blue). c,d Zoomed-in view of the (c) DFG motif and (d) αC helix in PEAK3, overlayed on the structure of PKA (PDB ID: 1ATP), aligned along entire kinase domain. e Zoomed-in view of the packing between the αC helix and activation loop of PEAK3 and the 14-3-3ε monomer. f Zoomed-in view of the pseudoactive site of PEAK3 showing the occluded nucleotide-binding site, the orientation of the catalytic lysine and the substituted Gln 221 in the αC helix.