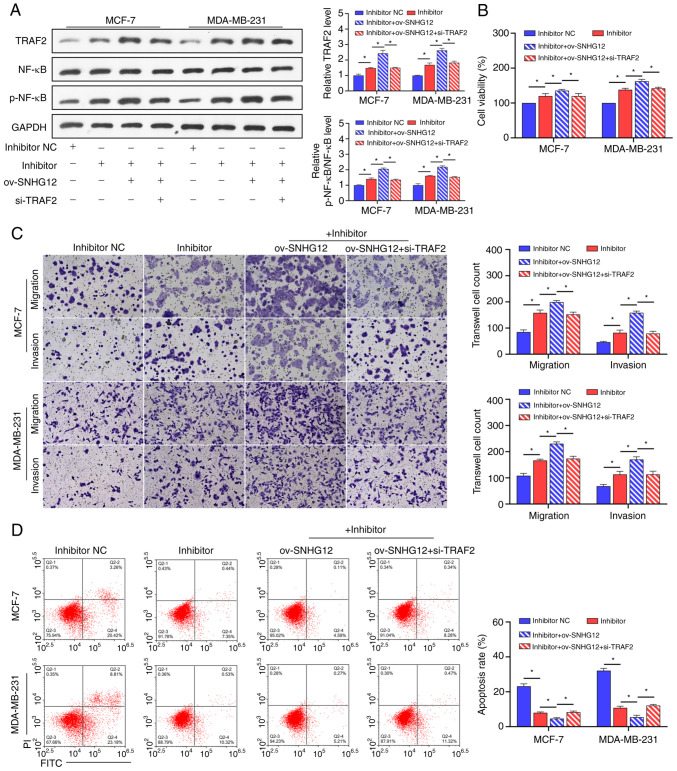
Figure 6.
SCO regulates the NF-κB signaling pathway through the SNHG12/miR-140-3p/TRAF2 axis to inhibit BC cell growth. (A) Western blot analysis of the effect of the interaction between ov-SNHG12, miR-140-3p inhibitor, and si-TRAF2 on protein levels of TRAF2, NF-κB, and p-NF-κB in the presence of SCO. (B) CCK8 analysis of the effect of the interaction between ov-SNHG12, miR-140-3p inhibitor, and si-TRAF2 on BC cell viability in the presence of SCO. (C) Transwell analysis of the effect of the interaction between ov-SNHG12, miR-140-3p inhibitor, and si-TRAF2 on BC cell migration/invasion in the presence of SCO. Magnification, x200. (D) FCM analysis of the effect of the interaction between ov-SNHG12, miR-140-3p inhibitor, and si-TRAF2 on BC cell apoptosis in the presence of SCO. *P<0.05. SCO, scoparone; BC, breast cancer; lncRNA, long non-coding RNA; SNHG12, small nucleolar RNA host gene 12; ov, overexpression; TRAF2, receptor-associated factor 2; RT-qPCR, reverse transcription-quantitative PCR; NC, negative control; miR, microRNA; Bio, biotinylated; ceRNA, competing endogenous RNA; si, small interfering; NF-κB, nuclear factor κB; FCM, flow cytometry; FITC, fluorescein isothiocyanate; PI, propidium iodide.