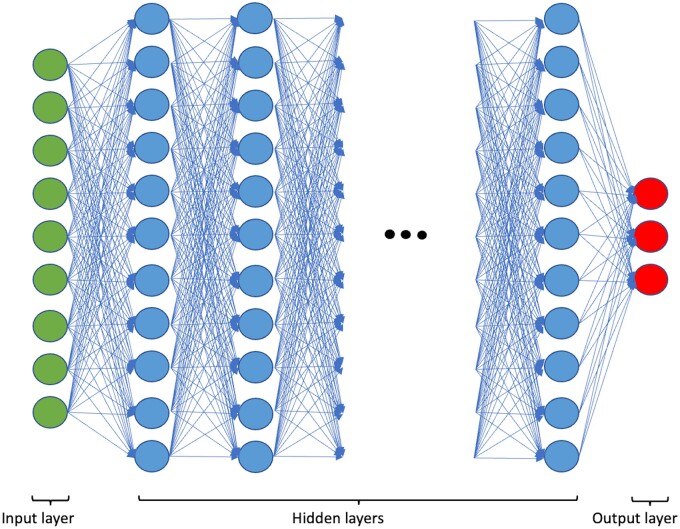
Figure 2.
Basic neural network architecture. The Input layer represents the data which is handed to the network as pixel values. The hidden layers can have an arbitrary number, the depth of the networks correlates with the computational burden. The dynamic adaption of weights during the training process happens in the hidden layers. Each neuron represents a covariable of the final transformation function learning by the network. The output layer is the output of the final computation, for example the classification of data into different labels. In the case of classification problems, it outputs a single label, while in segmentation problems it outputs pixels with a label assigned to each individually, which are then reconstructed into the final image.