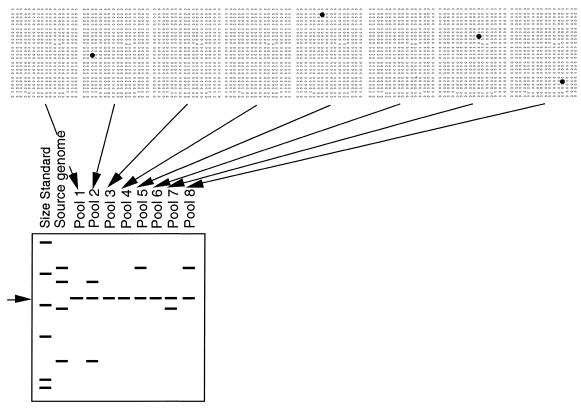
Figure 1.
BAC-RF method. Pooled BAC DNA is isolated from 384 BACs simultaneously, digested with a restriction enzyme, separated by electrophoresis, blotted and labeled with the cloned insert of a target DNA probe (to minimize hybridization to the BAC vector, the 7.1 kb band common to all pools is indicated by an arrow on the left). Differences in the size of restriction fragments are the basis for assigning BACs to individual loci in the source genome (second lane). Multiple restriction fragments that correspond to a single genetic locus co-occur in the same pools (2). Pools that lack a positive BAC show only the vector band (1, 3, 4 and 6). If robotic gridding of BACs is available, it is practical to probe dot blots and digests simultaneously. Lacking robotic gridding, by first screening digests, one need only screen the subset of dot blots for the pools that contain a positive clone.