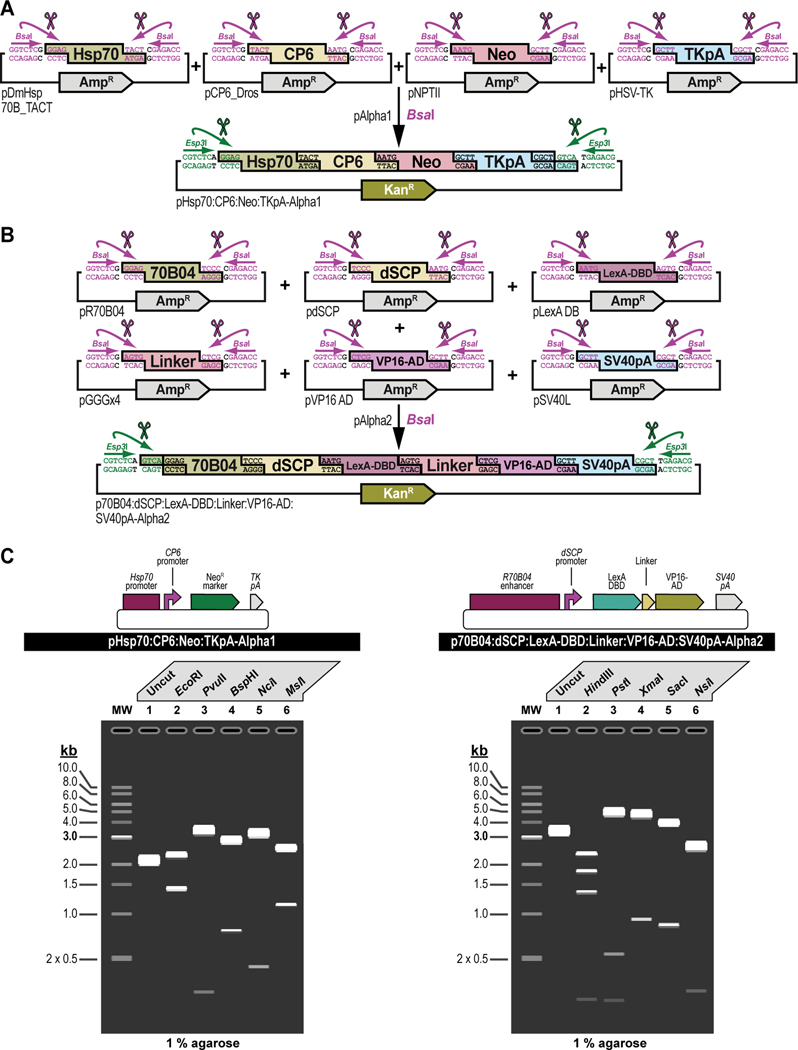
Figure 10. Practical examples of synthetic assembly cloning of multiple DNA parts into multipartite transcription units. (A) Synthetic assembly cloning of the transcription unit Hsp70:CP6:Neo:TKpA into pAlpha1.
Synthetic assembly cloning of four parts, the Hsp70 promoter from Drosophila melanogaster (Hsp70), the synthetic Escherichia coli CP6 promoter (CP6), the Neomycin phosphotransferase II of transposon Tn5 (Neo), and the minimal polyadenylation signal of the thymidine kinase gene from the herpes simplex virus (Tk pA) (see Figure 3), in the destination vector pAlpha1 dictated by their grammar identities (see Figure 2B) results in the transcription unit Hsp70:CP6:Neo:TkpA, one of the units used to build the G418 sulfate-selectable LexA transactivator plasmid (see Figure 3). (B) Synthetic assembly cloning of the transcription unit R70B04:dSCP:LexA-DBD:Linker:VP16-AD:SV40pA into pAlpha2. Synthetic assembly cloning of six parts, the R70B04 enhancer from Drosophila melanogaster (70B04), the Drosophila melanogaster synthetic core promoter (dSCP), the DNA binding domain of the LexA repressor from Escherichia coli (LexA-DBD), a (GlyGlyGlySer)4 peptide linker (Linker), the transcription factor activation domain of VP16 from the herpes simplex virus (VP16-AD), and the late polyadenylation signal from simian vacuolating virus 40 (SV40pA) (see Figure 3), in the destination vector pAlpha2 dictated by their grammar identities (see Figure 2B) results in the transcription unit R70B04:dSCP:LexA-DBD:Linker:VP16-AD:SV40pA, a second unit used to build the G418 sulfate-selectable LexA transactivator plasmid (see Figure 3). (C) Verification of synthetic assembly cloning of transcription units. Simulated gels showing restriction enzyme DNA fingerprinting for the transcription units assembled in pAlpha destination vectors: transcription unit Hsp70:CP6:Neo:TkpA assembled in pAlpha1 (pHsp70:CP6:Neo:TKpA-Alpha1) (Left, Top), and transcription unit R70B04:dSCP:LexA-DBD:Linker:VP16-AD:SV40pA assembled in pAlpha2 (p70B04:dSCP:LexA-DBD:Linker:VP16-AD:SV40pA-Alpha2) (Right, Top). Appropriate assembly for pHsp70:CP6:Neo:TKpA-Alpha1 is confirmed after restriction enzyme DNA fingerprinting using no enzyme to show uncut (Lane 1), and digestions using enzymes EcoRI-HF (Lane 2), PvuII-HF (Lane 3), BspHI (Lane 4), NciI (Lane 5), and MslI (Lane 6) (Left, Bottom). Appropriate assembly for p70B04:dSCP:LexA-DBD:Linker:VP16-AD:SV40pA-Alpha2 is confirmed after restriction enzyme DNA fingerprinting using no enzyme to show uncut (Lane 1), and digestions using enzymes HindIII-HF (Lane 2), PstI-HF (Lane 3), XmaI (Lane 4), SacI-HF (Lane 5), and NsiI-HF (Lane 6) (Right, Bottom). Digestions are visualized on a 1% agarose gel.