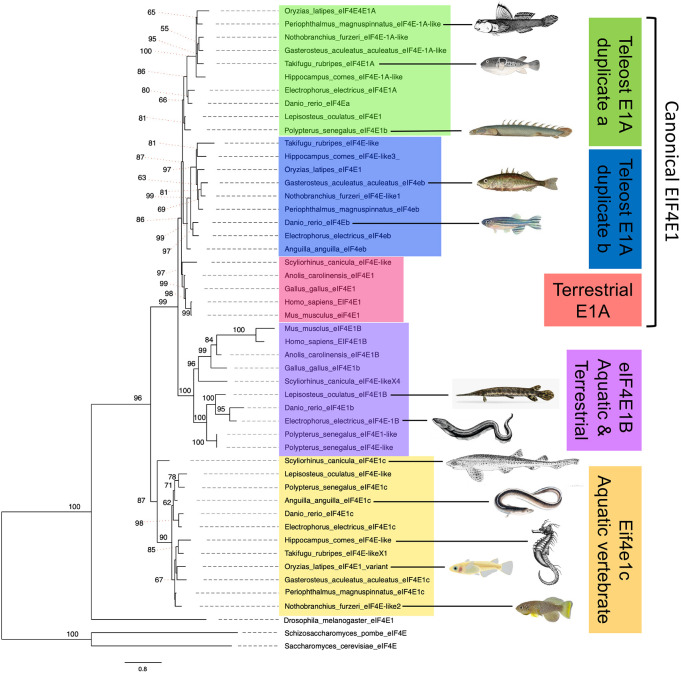
Fig. 1.
Eif4e1c is both unique to and shared by all aquatic vertebrates. Shown is a phylogeny of eIF4E1 orthologs from a sampling of the species considered (see Fig. S1 for full analysis). Eif4e1c is ancestral to the canonical eIF4E1A split from its variant, eIF4E1B. Terrestrial species have a canonical and eIF4E1B ortholog (pink and purple). All aquatic species have a canonical variant: eight species with a duplication (blue and green), two species retain only one variant of the duplication, and the Scyliorhinus canicula (small-spotted catshark) canonical clusters with terrestrial eIF4E1A. All 12 aquatic vertebrate retain an Eif4e1c family member. Shown are images of each of the aquatic vertebrate species to highlight the diversity considered. Only five of 12 aquatic vertebrates shown here retain an eIF4E1B variant. Estimates are made using maximum likelihood and the IQ-TREE. Nodes with bootstrap support <0.85 are marked with their respective values, all other nodes had support values of 0.85 or higher.