Fig 5. cBAF is required for targeting of T-bet to enhancers in effector CD8+ T cells.
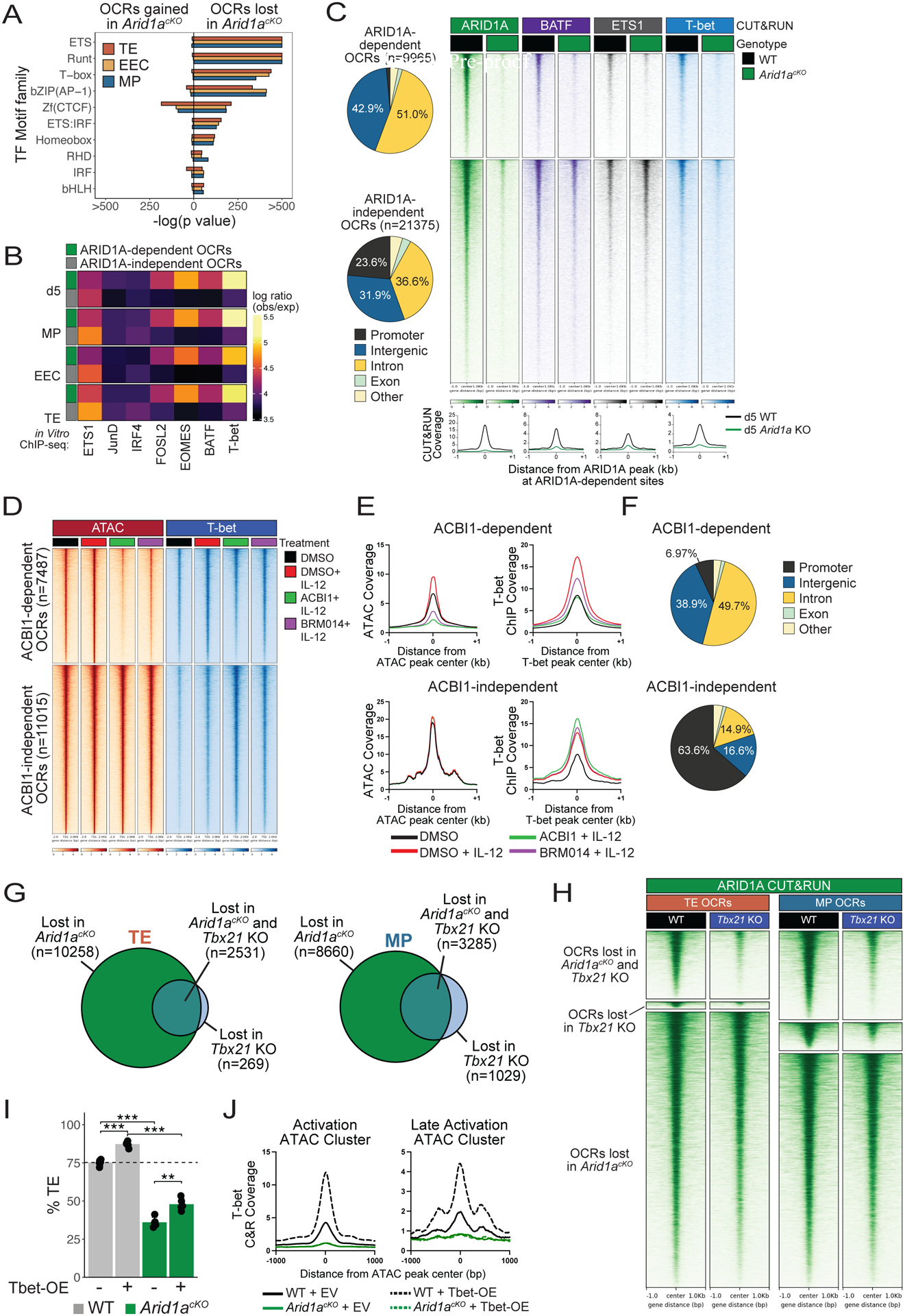
(A-B) As described in Figure 4, OCRs (2-fold change, adjusted p value<0.05, Benjamini-Hochberg) lost in Arid1acKO d5 effector cells or d8 TE, EEC, and MP subsets relative to WT cells were analyzed for enrichment of predicted TF motifs (A) or TF binding signals (observed/expected) of indicated TFs from public ChIP-seq datasets (GSE192390) in ARID1A-dependent (green) and - independent (gray) OCRs (B). (C) Genomic annotations and CUT&RUN signal heatmaps of ARID1A, BATF, ETS1, and T-bet at ARID1A-dependent or -independent OCRs from WT and Arid1acKO effector P14 CD8+ T cells d5 post-infection. (D-F) CD8+ T cells were activated in vitro for 48hrs and then treated with DMSO (black, red), ACBI1 (green) or BRM014 (purple) for 4 hours, and then treated with IL-12 (red, green, purple) for 2 hours, and analyzed for changes in ATAC-seq and T-bet binding by ChIP-seq. Signal coverage heatmaps of ATAC-seq and T-bet ChIP-seq (D) and histograms measuring chromatin accessibility (E) are shown. (F) Genomic annotations of ACBI1-dependent and -independent ATAC-seq OCRs. (G) Overlap of OCRs lost relative to WT (2-fold change, adjusted p value<0.05, Benjamini-Hochberg) in Arid1acKO or Tbx21 KO TE and MP cells. (H) ARID1A CUT&RUN signal heatmap in WT or Tbx21 KO effector cells at d5 p.i. Signal is centered on ARID1A- or Tbet-dependent OCR peaks identified in (G). (I) Retroviral overexpression of T-bet fails to rescue TE formation in Arid1acKO cells at d8 p.i. (J) T-bet CUT&RUN signal coverage histograms at Activation and Late Activation OCRs in WT or Arid1acKO cells transduced with either empty vector (EV) or T-bet overexpression (Tbet-OE) retrovirus at d5 p.i.*p<0.05, **p<0.005, ***p<0.0005.
