Fig 6. ARID1A is critical for Trm formation.
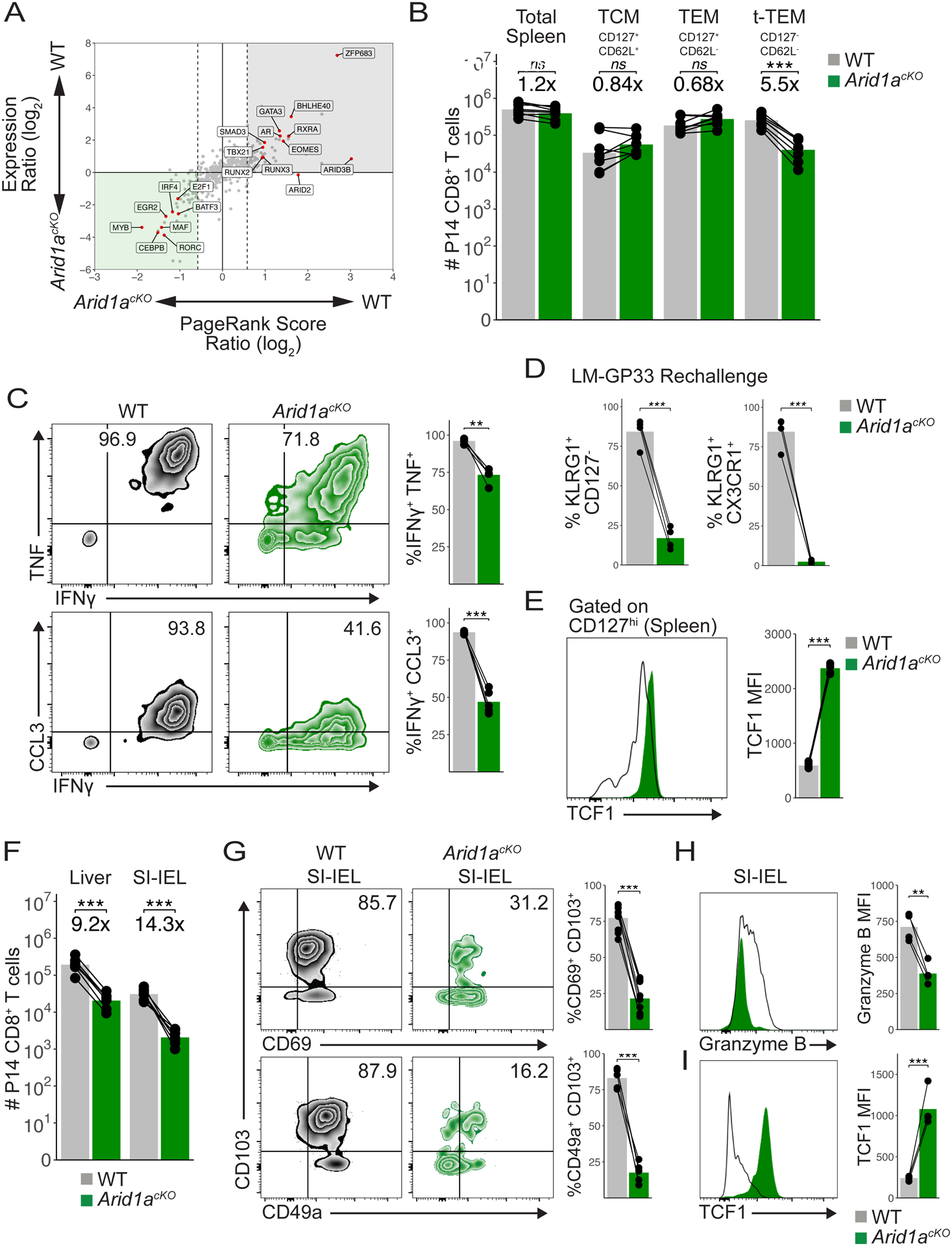
(A) PageRank and mRNA expression analysis of Arid1acKO and WT MP cells from d8 p.i. (B) Absolute numbers of WT (n=8) and Arid1acKO (n=8) P14 splenic memory cells at d30-d60 p.i. (C) Representative cytokine production in WT (n=4) and Arid1acKO (n=4) memory P14 cells in the spleen at d60 p.i. Mean frequency of IFNg+TNF+ (top) and IFNg+CCL3+ (bottom) populations are shown. (D) Frequency of KLRG1+CD127− or KLRG1+CX3CR1+ secondary effector cells 8d p.i. following LM-GP33 infection in mice that previously received CD127+ WT and Arid1acKO LCMV memory P14 cells. (E) TCF1 staining in WT and Arid1acKO CD127hi spleen memory cells at d50 p.i. (F) Absolute numbers of WT and Arid1acKO P14 cells in the liver (n=7) and SI-IEL (n=7) at d50-d60 p.i. (G) Representative flow cytometry plots of WT and Arid1acKO P14 SI-IELs at d60 p.i. Mean frequency of CD69+CD103+ (top) and CD49a+CD103+ (bottom) populations are shown. Granzyme B (H) and TCF1 (I) staining in WT and Arid1acKO P14 SI-IELs at d60 p.i. Paired t-test; *p<0.05, **p<0.005, ***p<0.0005.
