Figure 2.
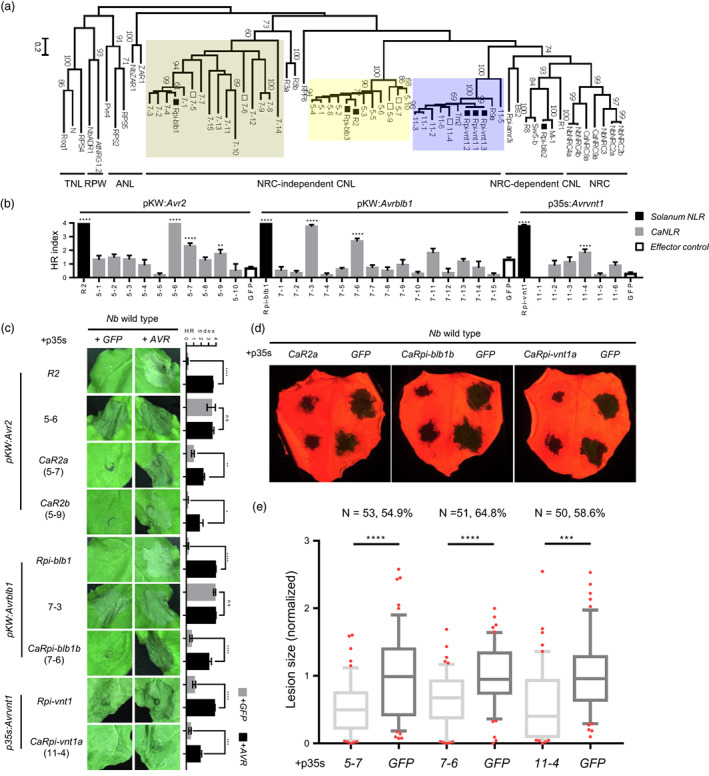
Multiple pepper NLRs homologous to R2, Rpi‐blb1, and Rpi‐vnt1 trigger HR against Avr2, Avrblb1, and Avrvnt1 and confer resistance to P. infestans in N. benthamiana. (a) Phylogenetic analysis of known R genes with CaNLR homologues. The tested CaNLR clades are coloured with boxes. Reference R genes and identified CaNLRs are marked with black and white rectangles at the end of nodes. (b) HR intensities of the 10, 15, and 6 pepper NLRs that are homologous to corresponding R genes of Avr2 (R2), Avrblb1 (Rpi‐blb1), and Avrvnt1 (Rpi‐vnt1), respectively, when co‐expressed with each effector. Several NLRs exhibited significant cell death phenotypes, marked with an asterisk (*), against each corresponding effector compared to GFP‐expressed cases as a negative control (white bars). Statistical significance was analysed using the unpaired t‐test (error bars indicate SEM from at least three replicates for non‐significant cases and at least 10 replicates for significant cases; **P < 0.005; ****P < 0.0001). (c) Representative images and HR intensity graphs of identified CaNLRs. CaNLR5‐6 and CaNLR7‐3 exhibited autoactive cell death when expressed with GFP in N. benthamiana. Statistical significance was analysed using the unpaired t‐test (error bars indicate SEM from at least four replicates; ns, nonsignificant; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.005; ***P < 0.0005; ****P < 0.0001). (d) Expression of CaNLR5‐7 (CA04g17640), CaNLR7‐6 (CA01g31430), and CaNLR11‐4 (CA03g00800) consistently reduced lesion size of P. infestans in N. benthamiana compared to GFP‐expression in the other half of the same leaves. (e) Average lesion sizes measured in three independent experiments are presented with 10–90 percentile box plots. Relative lesion sizes compared to those in GFP‐expression in the other half of the same leaves are marked with percentages on the top of each graph. Statistical significance was analysed using the unpaired t‐test (***P < 0.0005; ****P < 0.0001).
