Figure 1.
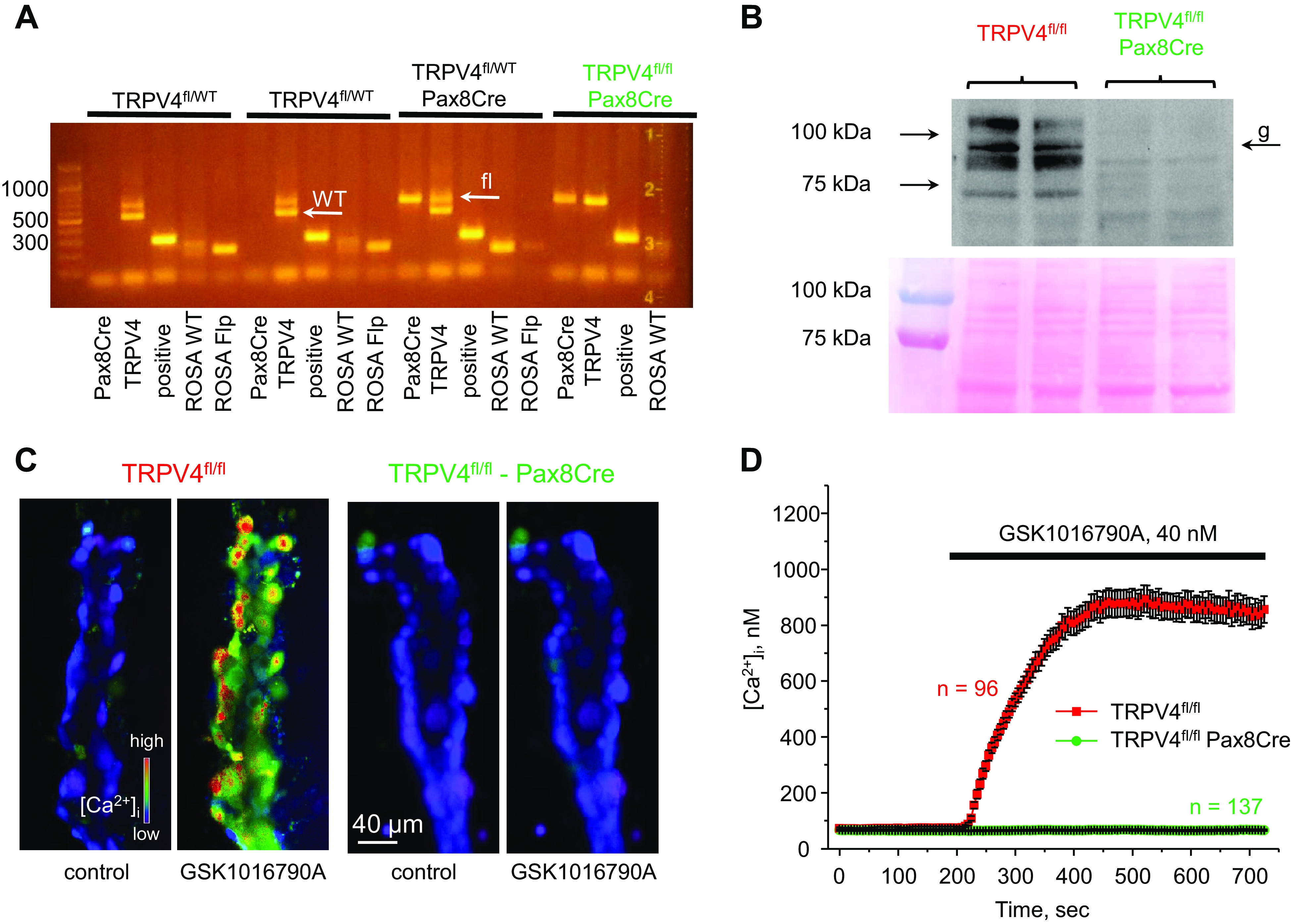
Verification of successful transient receptor potential vanilloid type 4 (TRPV4) deletion in the renal tubule. A: representative PCR genotype analysis of transgenic littermates probed with primers for Pax8Cre, TRPV4, and ROSA Flp, as described in methods. The desired genotype (TRPV4fl/fl-Pax8Cre, highlighted in green) contained positive reaction for Pax8, the presence of an upper loxP (fl) allele, and the absence of a lower wild-type (WT) allele for TRPV4, as indicated by white arrows. B, top: representative Western blot probed with anti-TRPV4 antibodies from whole kidney lysates of TRPV4fl/fl and TRPV4fl/fl-Pax8Cre mice (1 female and 1 male) showing the complete absence of a TRPV4-reporting signal. TRPV4 appeared as a duplet of bands around 95 kDa with the higher band representing a heavy mannitol sugar glycosylation form (shown as “g”). Each line represents an individual mouse. B, bottom: Ponceau red staining of the same nitrocellulose membrane demonstrating equal protein loading. C: representative pseudocolor images of intracellular Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]i) changes (blue: low and red: high) in isolated split-opened collecting ducts loaded with the Ca2+-sensitive dye Fura2 at baseline (left) and following 5-min application of 40 nM of the TRPV4 agonist GSK1016790A (right) from TRPV4fl/fl and TRPV4fl/fl-Pax8Cre mice. D: averaged time courses of [Ca2+]i changes upon application of 40 nM GSK1016790A (shown by the horizontal bar) in individual collecting duct cells within split-opened area from TRPV4fl/fl (red) and TRPV4fl/fl-Pax8Cre (green) mice. Each time point is shown as means ± SE. Numbers of individual cells are shown. Data were obtained from four different collecting ducts isolated from three different mice (2 females and 1 male) for each group.
