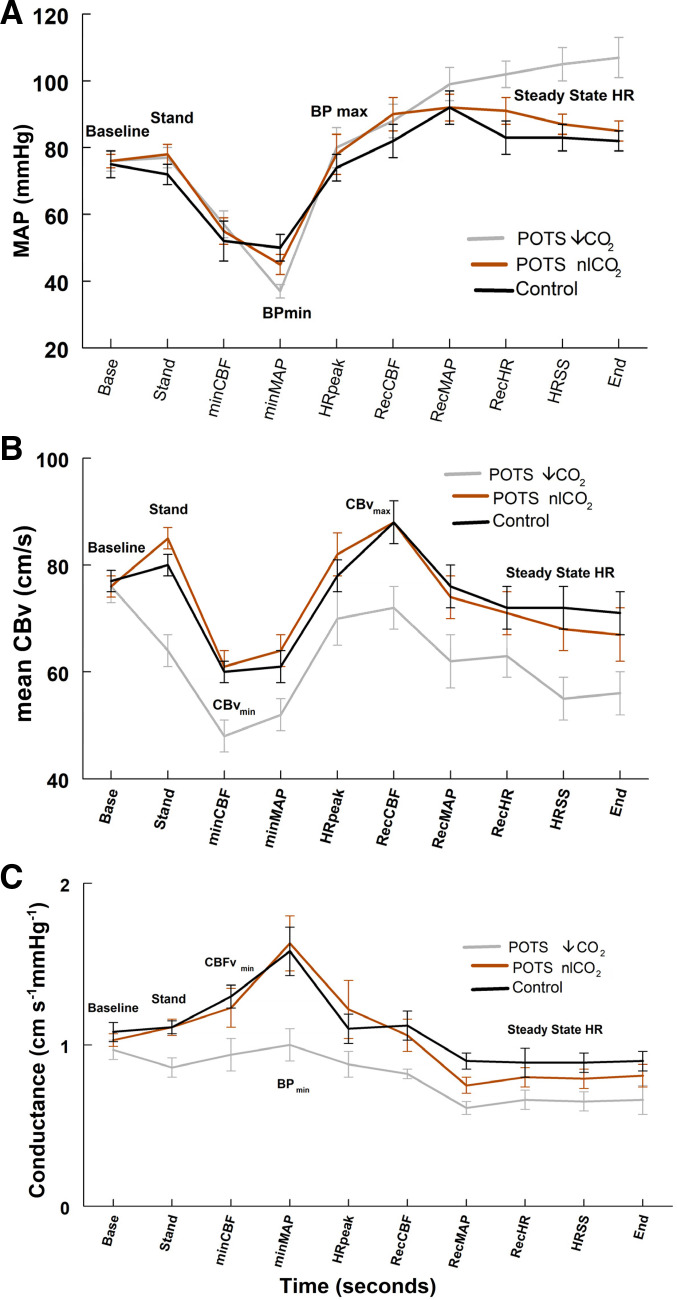
Figure 3.
Mean arterial pressure (MAP, A), mean cerebral blood velocity (mCBv, B), and cerebral conductance (C) for postural tachycardia syndrome with low end-tidal carbon dioxide (POTS-↓ETCO2) (in gray), postural tachycardia syndrome with normal upright end-tidal carbon dioxide (POTS-nlETCO2) (in red), and Control (in black). Reduced conductance maintains decreased mCBv in POTS-↓ETCO2. While the middle panel shows no significant differences for a group-by-time interaction, however, main effects for group and time were significant (P < 0.05). The bottom panel shows a significant group-by-time interaction for conductance (P < 0.05). Specifically, the POTS ↓CO2 had significantly a lower mean conductance value at the blood pressure (BP)min time point (adjusted P < 0.01).