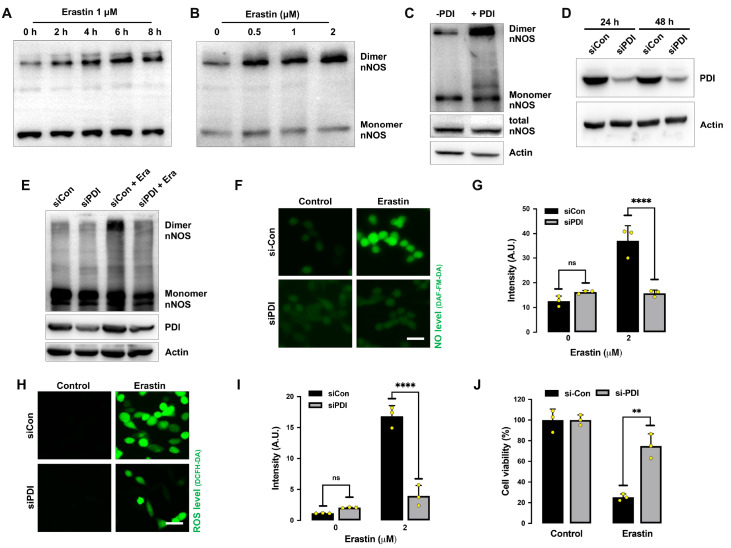
Figure 5 .
PDI knockdown protects HT22 cells against erastin-induced ferroptosis
(A,B) Levels of dimer and monomer nNOS after treatment with 1 μM erastin for the indicated time intervals (A) or at the indicated concentrations for 8 h (B). (C) Levels of dimer and monomer nNOS after incubation of cell lysates with PDI (1 mg/mL) in vitro at 4°C for 60 min. (D) Effectiveness of PDI-siRNA in reducing cellular PDI protein levels. Cells were transfected with PDI-siRNA for 48 h, and the PDI levels were determined by western blot analysis. (E) Effect of PDI knockdown on erastin-induced nNOS dimerization. Cells were transfected with PDI-siRNA for 24 h prior to treatment with 1 μM erastin for an additional 24 h. nNOS dimer formation was detected by western blot analysis. (F‒J) Effect of PDI knockdown on erastin-induced NO and ROS accumulation. Cells were transfected with PDI-siRNA for 24 h prior to erastin (1 μM) treatment. The levels of NO and ROS after 8 h of erastin treatment were assessed by fluorescence microscopy (F,H), and their quantitative intensity values are shown in G and I. Cell viability changes were analysed after 24 h of erastin treatment (J). Scale bar: 45 μm. Data are presented as the mean±SE. n=3. * P<0.05, ** P<0.01 vs the control group.