Fig. 5. Potential effects of CD137 agonist treatment on t cell exhaustion, activation, and trafficking.
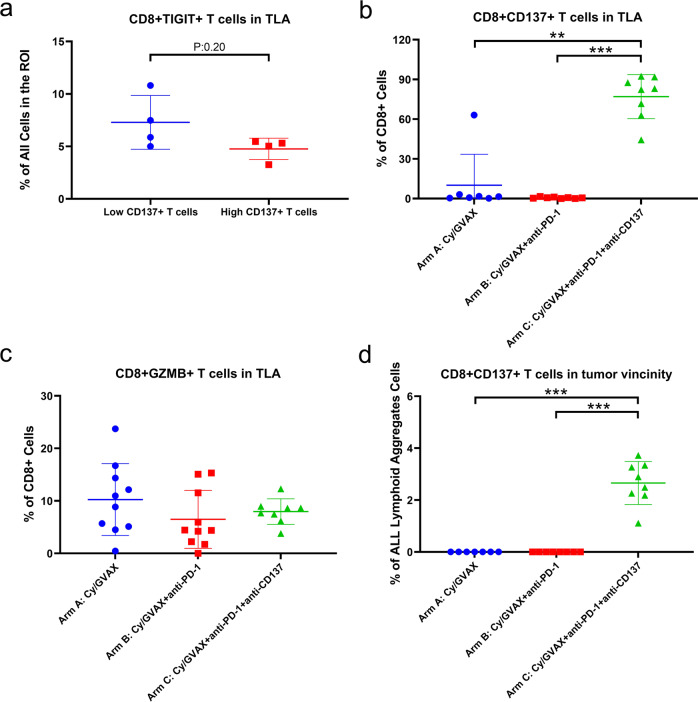
a Samples in Arm C were subgrouped, according to the density of CD137+ CD8+ T cells in TLAs by using the mean of the density as cutoff, into two cohorts: low (n = 4) vs. high (n = 4) CD137+ T cells. The density of CD45+ CD3+ CD8+ TIGIT+ T cells was compared between the two cohorts. b The percentage of CD45+ CD3+ CD8+ CD137+ T cells among CD45+ CD3+ CD8+ T cells was compared between treatment arms. GVAX (Arm A) vs GVAX+PD-1+CD137 (Arm C): p = 0.0012, GVAX+PD-1 (Arm B) vs. GVAX+PD-1+CD137 (Arm C): p = 0.0002. Arm A: n = 7; Arm B: n = 8; Arm C: n = 8. c The percentage of CD45+ CD3+ CD8+ GZMB+ T cells among CD45+ CD3+ CD8+ T cells was compared between treatment arms. Arm A: n = 10; Arm B: n = 10; Arm C: n = 8. d The density of CD45+ CD3+ CD8+ CD137+ T cells in the tumor vicinity area outside TLAs, calculated as the percentage among all cells, was compared between treatment arms, GVAX (Arm A) vs GVAX+PD-1+CD137 (Arm C): p = 0.0003, GVAX+PD-1 (Arm B) vs. GVAX+PD-1+CD137 (Arm C): p = 0.0002. Arm A: n = 7; Arm B: n = 8; Arm C: n = 8. All data shown as the mean ± SD. Treatment arms as indicated. Two-sided Mann–Whitney tests were performed; p values were shown: *<0.05; **<0.01; ***<0.001; if not shown, non-significance. Multiplex IHC analysis was repeated twice with consistent results.