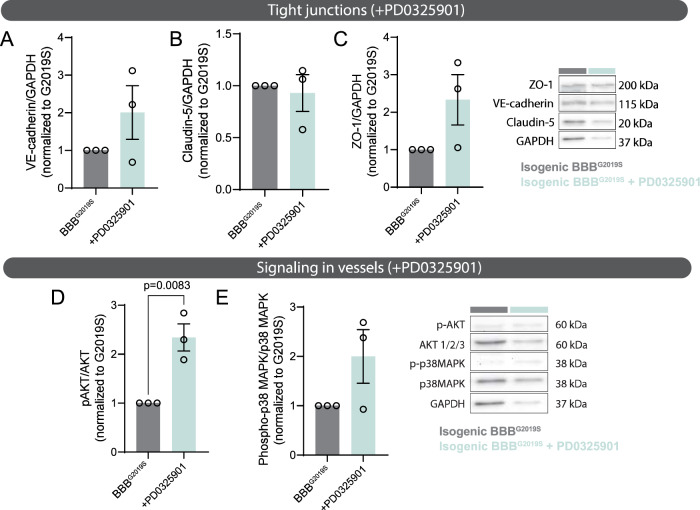
Fig. 7. Rescue of BBB function is associated with increased AKT phosphorylation in the vessels.
A–C Immunoblots showing protein levels of tight junction markers VE-cadherin (A), claudin-5 (B), ZO-1 (C), and loading control GAPDH in lysates extracted from the vascular compartment of BBBG2019S chips in which the brain compartment was treated with regular growth medium or medium supplemented with 0.5 µM PD0325901 for 6 days. Protein levels are normalized to GAPDH loading control and data is shown as the fold change of treated vs. untreated BBBG2019S vessels. D, E Immunoblots reporting protein levels of phosphorylated AKT, total AKT (D), phosphorylated p38MAPK, total p38 MAPK (E), or loading control GAPDH in lysates extracted from the vascular compartment of BBBG2019S chips in which the brain compartment was treated with regular growth medium or medium supplemented with 0.5 µM PD0325901 for 6 days. Protein levels are normalized to GAPDH loading control and data are shown as the fold change of treated vs. untreated BBBG2019S vessels. Data are from three biological replicates; error bars represent mean + SEM. Statistical analysis was performed using two-tailed unpaired Student’s t test with equal s.d. The BBBG2019S nomenclature refers to the presence of LRRK2 G2019S astrocytes in the brain compartment of the BBB chip. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.