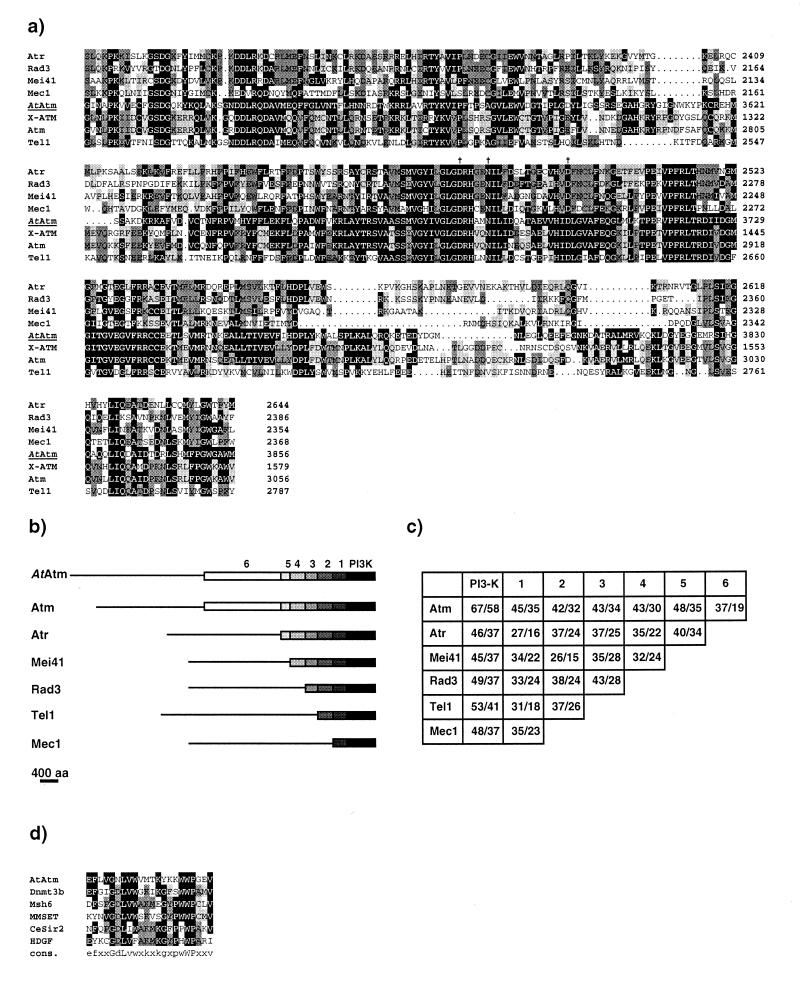
Figure 2.
(a) Alignment of the C-terminal region spanning the Pi3 kinase-like domain of AtAtm with six closely related members of the Atm family. The numbers on the right indicate the position of the residues for each protein. Amino acids identical to AtAtm are boxed in black. Pale and dark grey boxes highlight amino acid identities between two and three or more proteins respectively, AtAtm excluded. The alignment was performed with the PILEUP program (Genetics Computer Group, v.9.1). Vertical arrows indicate the three conserved residues of the kinase catalytic site, namely Asp 3681, Asn3686 and Asp3700 for AtAtm. (b) Schematic drawing for the alignment of the AtATM translation product to related protein in mammals (Atm, Atr), Drosophila melanogaster (Mei41) and yeast (Rad3, Tel1 and Mec1). Sequences were drawn to scale. Black boxes cover the Pi3-kinase-like region of strong homology, which is shared by all family members; boxes 1–5, the different homology domains between each protein and AtAtm; box 6, the region of similarity shared by AtAtm and Atm only. Thin lines for each sequence indicate region with no similarity (<20% identity). Alignments were performed agains thet AtAtm sequence with each of the family members using the GAP program (Genetics Computer Group, v.9.1). (c) Percentages of amino acid similarity and identity for the domains defined in (b) between the different Atm-related proteins. In each box, the first number represents the similarity and the second number the identity. (d) Alignment of the PWWP domain of the following proteins: AtAtm, Dnmt3b (accession number AAF04015), hMsh6 (accession number AAB39212), MMSET type I (accession number AAF23369), Caenorhabditis elegans similar to Sir2 (accession number U97193), and HDGF (accession number P51858). The alignment was generated as in (a).