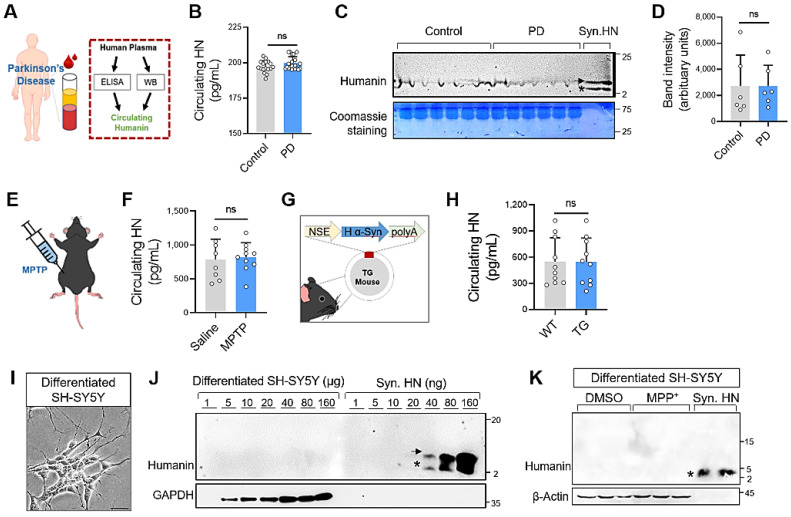
Figure 1.
Humanin protein levels are not correlate with Parkinson's disease. (A) Schematic of the study setup. (B, C, D) Circulating levels of humanin in the plasma of PD patients using ELISA (B) (n = 21 PD patients, n = 17 healthy control groups) and western blot analysis (C, D) (n = 6 per group). Circulating humanin in the plasma shows weak expression both in PD and control groups. Synthetic humanin peptide (Syn. HN: 100 ng). Asterisk and arrow indicate the monomeric (~3 kDa) and dimeric form (~ 6 kDa) of humanin, respectively. (E, F) Mouse model of PD treated with MPTP (20 mg/kg/day, ip) for 5 consecutive days. Two days after the final MPTP treatment, circulating humanin was measured in the plasma of MPTP-treated mice using ELISA. (G, H) Transgenic (TG) mouse models of PD overexpressing human α-synuclein gene (α-syn). Using ELISA, circulating humanin was assessed in the plasma of transgenic PD mice at the age of 10 - 12 months. (I) Phase-contrast pictures of differentiated SH-SY5Y cells. Scale bar, 20 μm. (J) Quantitative WB analysis of cell lysates from differentiated SH-SY5Y cells (1 - 160 μg) and synthetic humanin (HN) peptide (1 - 160 ng) by tricine-SDS-PAGE. (K) No clear alteration of intracellular humanin in SH-SY5Y cells against neurotoxin MPP+ exposure. Synthetic humanin peptide (Syn. HN: 100 ng). Data are expressed as mean ± SEM (standard error of the mean). NS: not significant; P > 0.05. WT: Wild-type.