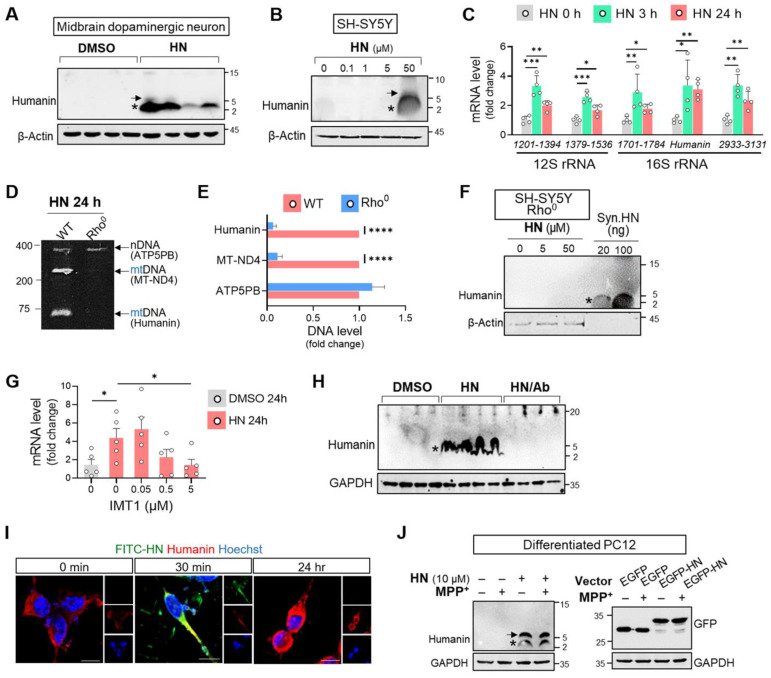
Figure 2.
Humanin treatment induces intracellular humanin expression in neuronal cells. (A, B) HN treatment for 24 h results in upregulation of intracellular humanin in mouse midbrain dopaminergic neurons (A) (1 μM) and SH-SY5Y cells (B) in dose-dependent manner. Asterisk and arrow indicate the monomeric and dimeric forms of humanin, respectively. (C) Real-time qPCR analysis amplifying different regions of the mitochondrial rRNAs (12S rRNA and 16S rRNA) after HN treatment for designated hours. Each value on the x-axis represents a targeted sequence within mitochondrial genome. (D, E) Conventional PCR with specific primers targeting nuclear DNA (nDNA; ATP5PB) and mitochondrial DNA (mt-ND4 or humanin) from Rho0 cells devoid of mtDNA. The bands on polyacrylamide gels were quantified. (F) Western blot analysis assessing intracellular humanin levels in SH-SY5Y Rho0 cells after HN treatment (20 μM) for 24 h. Synthetic humanin peptide (Syn. HN: 100 ng). (G) Real-time qPCR analysis by co-treating IMT1 inhibiting mitochondrial gene expression with HN in SH-SY5Y cells. (H) Western blot analysis with treating HN peptide (20 μM) with HN antibody (HN/Ab) in SH-SY5Y cells. HN/Ab mixture (3 times excess peptide to antibody by weight). (I) Immunofluorescence of fluorophores conjugated HN (FITC-HN: green) in SH-SY5Y cells for indicated hours. Intracellular humanin was stained (red). Scale bar, 10 μm. (J) Western blot of upregulated intracellular humanin by HN peptide or transfection with EGFP-tagged humanin expression plasmid (EGFP-HN) in differentiated PC12 cells. EGFP plasmid (EGFP). Data are expressed as means ± SEM. (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001). HN: humanin.