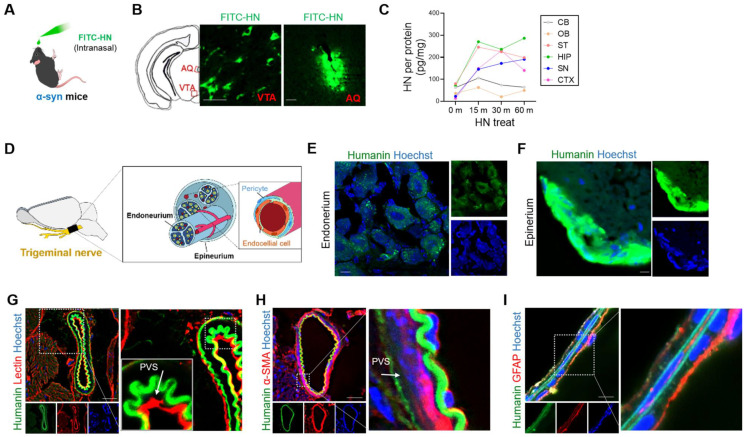
Figure 4.
Intranasally administered humanin can reach the brain via the trigeminal nerve along the perivascular and perineural spaces. (A) Schematic diagram of experiments performed after FITC-tagged humanin (FITC-HN) treatment of transgenic PD mice overexpressing human α-syn. (B) FITC-HN was detected in the midbrain regions including the ventral tegmental nerve (VTA) and cerebral aqueduct (AQ) within 30 m after intranasal administration. Scale bar, 50 μm. (C) ELISA for detecting FITC-HN in the brain tissue samples after intranasal administration at the indicated time points. CB, cerebellum; OB, olfactory bulb; ST, striatum; HIP, hippocampus; SN, substantia nigra; CTX, cerebral cortex. (D) Putative delivery route of FITC-HN distribution after intranasal injection to the brain through the trigeminal nerve. (E, F, G, H) Within 10 minutes after intranasal treatment, FITC-HN was detected associated with the epineurium (E) and, to a lesser extent, the endoneurium (F) of the trigeminal nerves as well as in the perivascular space (PVS), as evaluated by staining blood vessels with tomato lectin (G) and alpha smooth actin (α-SMA) (H). (I) Within 30 minutes after intranasal treatment, FITC-HN for brain was found in microvascular endothelial cells surrounded by astrocytic endfeet, stained with anti-glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP). Scale bar, 10 μm. HN: humanin.