Figure 1.
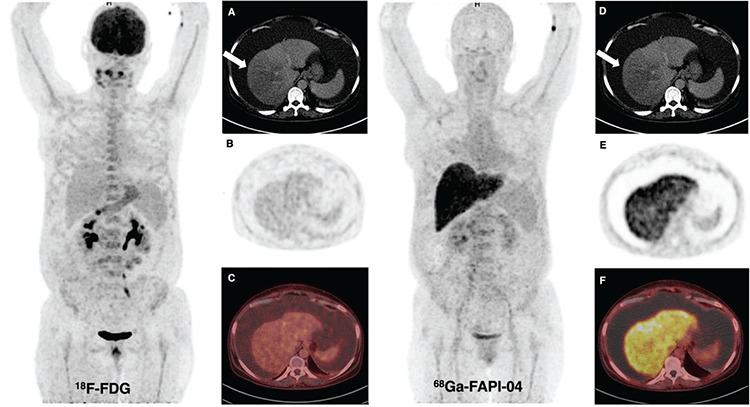
A 50-year-old woman patient presented with abdominal pain and was found to have massive ascites and had undergone18F-fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) and 68Ga-fibroblast activation protein inhibitor (FAPI)-04 positron emission tomography/computed tomography (PET/CT) imaging for a suspected gastric tumor. Abnormal liver activity was not observed on 18F-FDG PET/CT, but diffuse intense FAPI uptake [maximum standardized uptake value (SUVmax): 11.2] was seen in the liver on 68Ga-FAPI-04 PET/CT. The hypodense area detected in CT sections [(A, D) arrow] at the right lobe of the liver did not show prominent 18F-FDG [(B) PET, (C) fusion images] or FAPI uptake [(E) PET, (F) fusion images] in the parenchyma. Also, no malignant cells were found in the peritoneal aspiration fluid. The patient is being followed up with the diagnosis of decompensated alcoholic cirrhosis.
