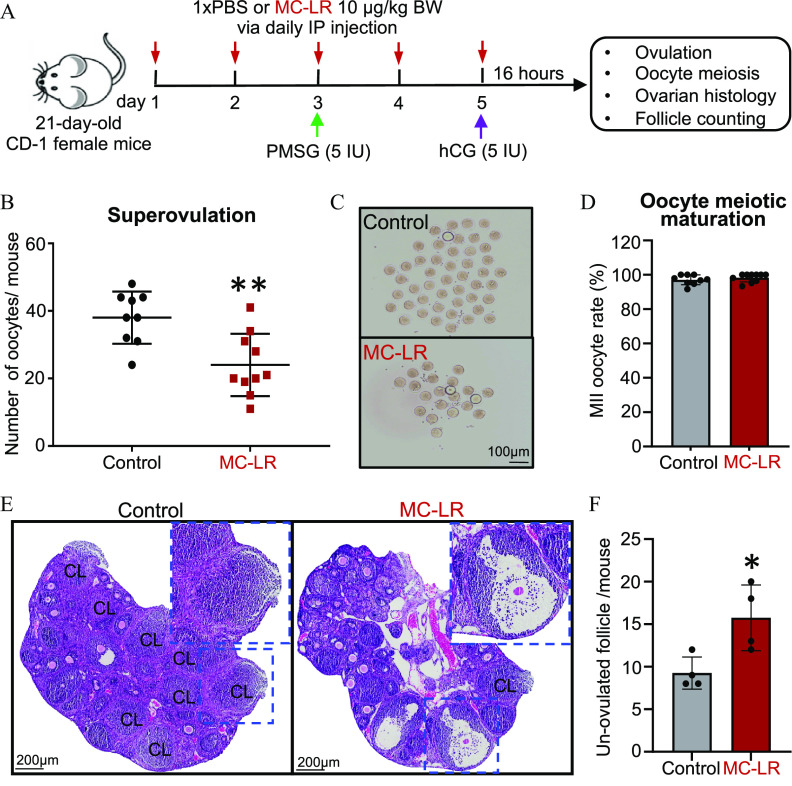
Figure 2.
Effects of acute exposure to MC-LR on follicle ovulation. (A) The schematic of intraperitoneal treatment of PBS () or MC-LR () in a mouse superovulation model. (B) Numbers and (C) representative images of ovulated oocytes from mice treated with PBS or MC-LR. (D) Percentages of ovulated MII oocytes in mice treated with PBS or MC-LR. (E) Representative ovarian histological images after ovulation induction in PBS- or MC-LR–treated mice. Blue dash squares indicate newly formed corpora lutea (CL) or un-ovulated late-staged antral follicles in PBS- or MC-LR–treated mouse ovaries, respectively. (F) Total numbers of un-ovulated late-staged antral follicles per mouse in PBS- or MC-LR–treatment groups. mice or 8 ovaries were randomly selected in each group for the histological staining and counting of un-ovulated follicles. Data were analyzed with Student’s -test (B,D,F). Bidirectional error bars represent ; * and **. Data in (B,D,F) are also presented in Tables S6–S8, respectively. Note: hCG, human chorionic gonadotropin; IP, intraperitoneal; MC-LR, microcystin-LR; MII, metaphase II; PBS, phosphate-buffered saline; PMSG, pregnant mare serum gonadotropin.