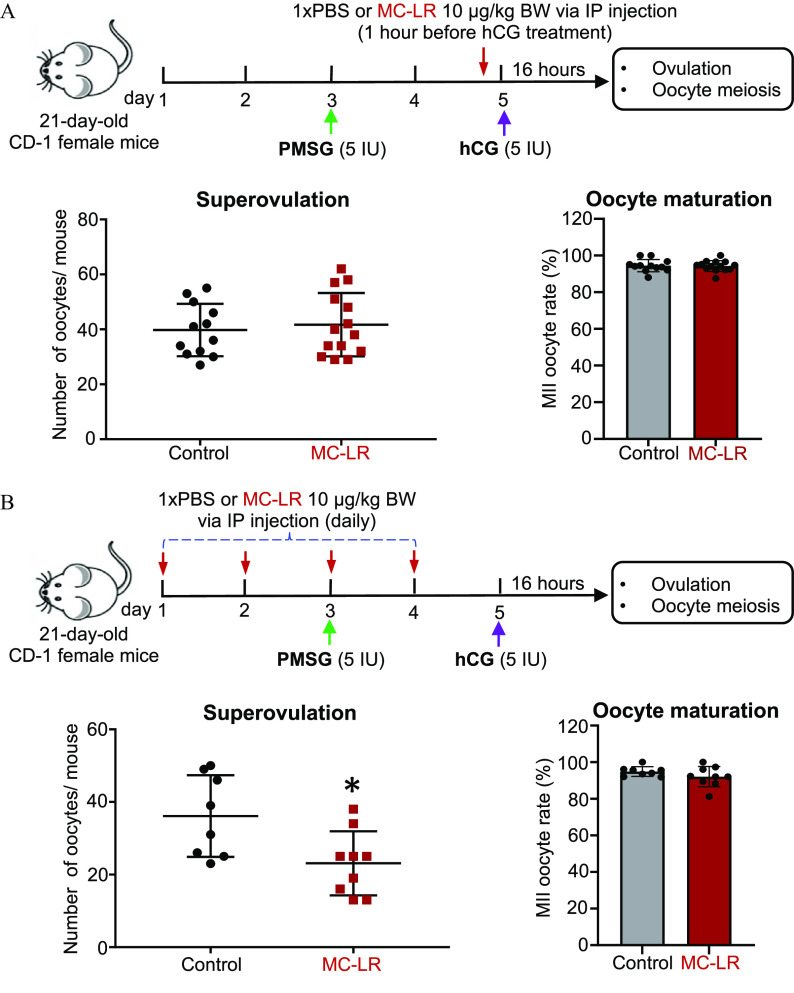
Figure 3.
Effects of acute MC-LR exposure during ovulation window and follicle maturation window on follicle ovulation. (A) The schematic of acute MC-LR exposure during the ovulation window. CD-1 female mice at 21-d-old were intraperitoneally treated with PBS () or MC-LR () at 1 h before hCG injection, and the numbers of ovulated oocytes and percentages of MII oocytes at 16 h post-hCG injection. (B) The schematic of acute MC-LR exposure during the follicle maturation window. CD-1 female mice (21-d-old) were intraperitoneally treated with PBS () or MC-LR () from day 1 to day 4, and the numbers of ovulated oocytes and percentages of MII oocytes at 16 h post-hCG injection were determined. Data were analyzed with Student’s -test (A,B). Bidirectional error bars represent ; *. Data in (A,B) are also presented in Tables S9 and S10, respectively. Note: hCG, human chorionic gonadotropin; IP, intraperitoneal; MC-LR, microcystin-LR; MII, metaphase II; PBS, phosphate-buffered saline; PMSG, pregnant mare serum gonadotropin.