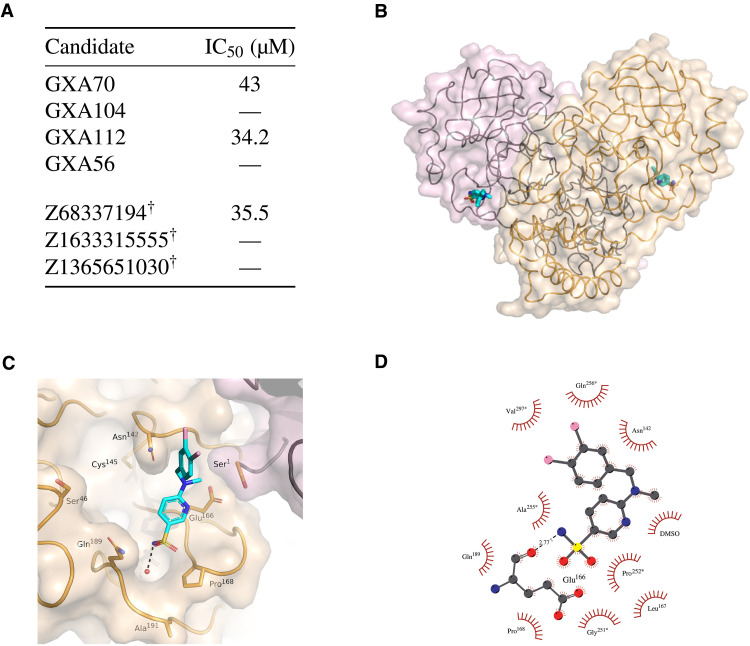
Fig. 6. Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 Mpro by machine-designed de novo and commercially sourced compounds.
(A) Half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) from RapidFire MS experiments for de novo and commercial Mpro inhibitor candidates. Symbol “—” indicates that no inhibition was detected. Candidates marked with † had successful crystal structures determined. (B to D) Crystal structure of the SARS-CoV-2 Mpro in complex with Z68337194. (B) Ribbon representation with transparent surface of the Mpro dimer colored in wheat and light pink to delineate each protomer. The active site of each protomer is shown with Z68337194 in stick representation. (C) Surface representation showing the overall binding mode of Z68337194 at the active site of Mpro. (D) Schematic representation of the interactions of Z68337194 with Mpro. Residues indicated with * are from a symmetry-related Mpro protomer.