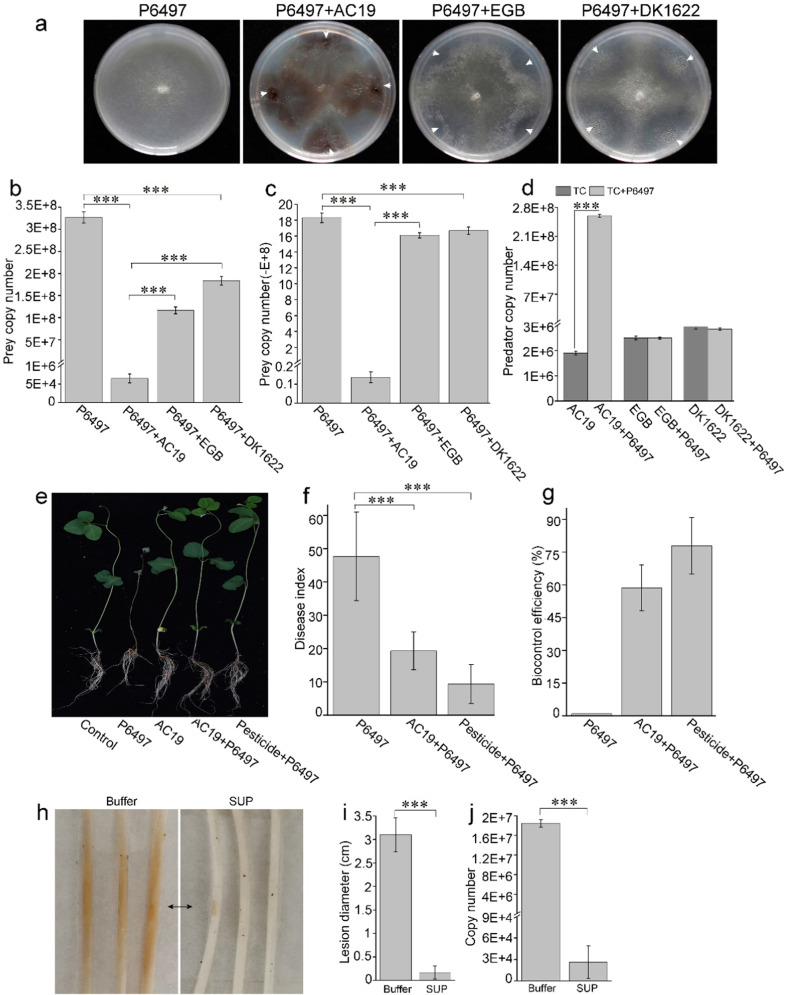
Fig. 1. Biocontrol of P. sojae by Archangium sp. AC19.
a Co-cultures of P. sojae P6497 against AC19, EGB or DK1622 on VY/4 plates. P6497 was cultured on VY/4 plates for 2–3 days (time to attain a colony diameter of 2 cm), and then myxobacteria were spotted near Phytophthora colonies and gown at 30 °C for 3 days. White arrow heads indicate the inoculation sites of myxobacteria. b Quantitative analysis of the biomass of P6497 from the solid plates by qPCR. P6497 was cultivated separately or co-cultured with indicated myxobacteria on VY/4 plates. Genomic DNAs were harvested from plates and P6497 biomass quantified. Biomass analysis of P6497 (c) and myxobacteria (d) was quantified from liquid TC media (TPM buffer, 0.1% casitone, pH 7.2) by qPCR. Indicated myxobacterial strains (1 × 105 cells/mL, final concentration) were incubated alone or with P6497 (50 mg, wet weight) in 20 mL TC media at 30 °C for 2 days. e Effects of P6497 infection in conjunction with AC19. Disease index (f) and biocontrol efficiency (g). All soybean seedlings were incised with a small wound and inoculated with 4-mm-diameter agar discs of P6497 with or without AC19 or pesticide except for the control sample. h–j Biocontrol efficacy of SUP in soybean hypocotyl infection assays. The agar discs (4-mm-diameter) of P6497 were pretreated with SUP (0.02 mg/mL) at 30 °C for 20 min before incubation. Representative photographs (h), average lesion diameters (brown color; three representative samples; black arrow indicates inoculation sites) (i) and quantitative biomass of P6497 (j) with standard errors shown. The biomass was measured by qPCR of genomic DNA with standard curves. Error bars denote ± standard error of the mean (SD), and asterisks (***) indicate statistically significant differences (p < 0.01) to control based on Student’s t test.