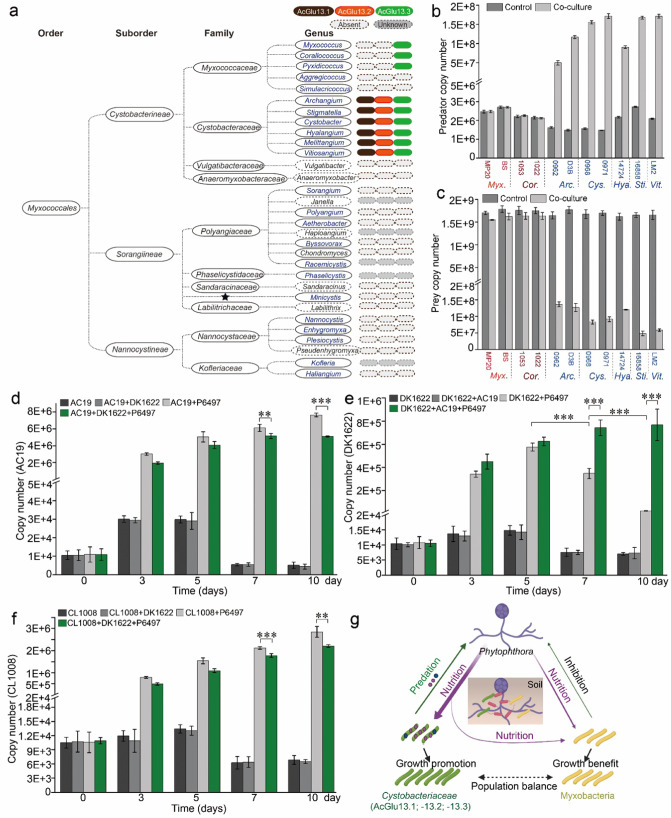
Fig. 8. Predation of P. sojae among Cystobacteraceae is correlated with the presence of the specialized glucanase consortium.
a Identification of AcGlu13.1-AcGlu13.2-AcGlu13.3 orthologs across the order Myxococcales. Genera that harbor or lack orthologs are indicated, dark gray ovals are genera with unavailable genome, ★ undesignated family affiliation, blue font documented predatory myxobacteria with ability to feed on bacteria and/or fungi. Co-culture assay of P. sojae P6497 with myxobacteria isolates across the families Cystobacteraceae and Myxococcaceae. Quantitative biomass of myxobacteria (b) and P6497 (c) from co-culture assays by qPCR. P6497 (50 mg, wet weight) was incubated with myxobacteria (1 × 105 cells/mL, final concentration) in 20 mL TC media at 30 °C for 3 days. Soil feeding experiments with mixtures of P6497 and AC19, DK1622 and CL1008 in non-sterile soil. Quantitative biomass of AC19 (d), DK1622 (e), CL1008 (f) from different culture mixtures and times (day 0, 3, 5, 7 and 10) by qPCR. (g) Suggested model of nutritional interaction between predatory (green) and non-predatory (yellow) myxobacteria taxa on Phytophthora (purple). Experimental scheme of the soil pot experiment was designed based on different mixtures of strains (Fig. S23a). Arrow intensities indicate relative impacts.