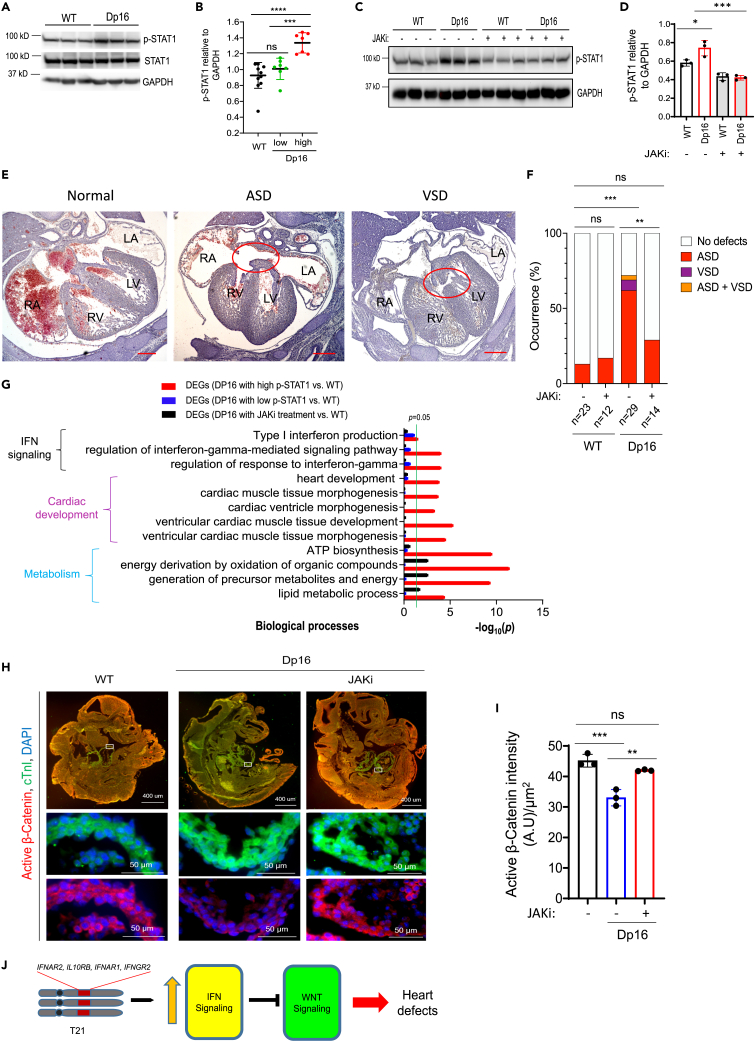
Figure 4.
Pharmacological inhibition of IFN signaling prevents heart malformations in Dp16 embryos
(A and B) Immunoblotting analysis of heart extracts from indicated embryos at E15.5 for p-STAT1, total STAT1, and GAPDH. Representative western blots are shown in A. Quantification of protein levels from western blots are in B. Each filled circle represents one individual embryonic heart. Data are presented as mean ± SD. ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001, ordinary one-way ANOVA.
(C and D) Immunoblotting analysis of heart extracts from indicated embryos at E15.5 for p-STAT1 and GAPDH. Pregnant mice were daily treated with the JAKi (10 mg/kg body weight/day, i.p. injection) beginning on day 6.5 post-conception. Hearts were harvested at E15.5 for analysis. Protein quantification is shown in D. Each filled circle represents one individual heart. Data are presented as mean ± SD. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, Ordinary one-way ANOVA.
(E and F) Histological analysis of cardiac septation in embryos at E15.5. Representative images of hematoxylin & eosin-stained sections of embryos are shown in E. Normal septation of four chambers in a WT embryo, and atrial septal defect (ASD) or ventricular septal defect (VSD), which were each observed in Dp16 embryos. LA, left atrium; RA, right atrium; LV, left ventricle; RV, right ventricle. Percentages of E15.5 embryos displaying heart malformations are shown in F. Scale bar, 300 μm. ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ns, not significant, Fisher’s exact test.
(G) GO analysis of the dysregulated DEGs, as assessed by RNA-seq, associated with variable IFN signaling and JAKi treatment. FPKM ≥30 in WT samples was set as cutoff to filter transcripts. DEGs were determined by Student’s t test (p < 0.05). N = 3–4 hearts for each group.
(H and I) Examination of cardiac troponin I (cTnI) and active β-Catenin levels in embryos at E9.5 by immunofluorescence (IF) analysis. Pregnant mice were treated daily with vehicle or the JAKi (10 mg/kg body weight/day, i.p.) beginning with day 6.5 post-conception. Embryos were harvested at E9.5 for IF analysis. Representative IF images are presented in H. Scale bars on top panels, 400 μm. Scale bars on middle and bottom panels, 50 μm. Each white box indicates area of magnification in bottom images. Quantification of IF signaling intensity for active β-Catenin in cTnI+ developing hearts in I. Two sections were analyzed for each embryo. Each filled circle represents the average of active β-Catenin signals in one embryo. ∗∗p < 0.05, ∗∗∗p < 0.05, ns, not significant, ordinary one-way ANOVA.
(J) T21 leads to increased expression of IFN receptors encoded by genes on HSA21, which overactivates IFN signaling. Activated IFN signaling decreases the activity of the canonical Wnt pathway, eventually leading to defects during heart development.