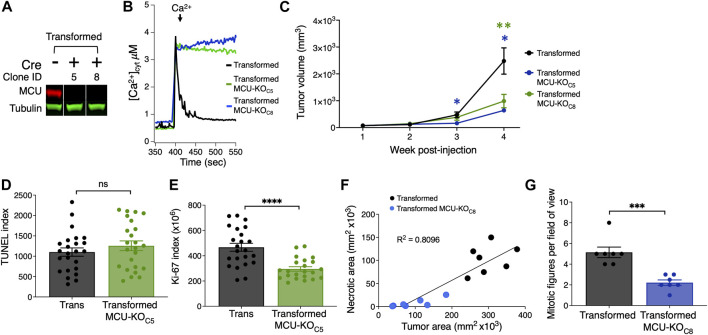
FIGURE 2.
Histological analyses of tumor xenografts reveal that deletion of MCU reduces proliferation and oncogenic potential of primary mouse fibroblasts in vivo. (A) Representative immunoblots of MCU and tubulin in transformed fibroblasts. Single MCU-KO clones selected from heterogeneous population of transformed fibroblasts expressing mCherry-Cre by FACS. (B) Representative traces of [Ca2+]cyt in cell suspensions of transformed MCU-KO clones to validate complete elimination of MCU-mediated mitochondrial Ca2+ uptake. (C) Volumes of tumor xenografts of transformed fibroblasts and MCU-KO fibroblasts during 4 weeks post-injection (mean ± SEM, n = 10, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, two-way ANOVA). (D) Quantification of TUNEL index in tumor xenografts as indicator of DNA damage due to cell death (mean ± SEM, n = 3, ns = non-significant, Student’s t-test). (E) Quantification of ki-67 index in tumor xenografts as indicator of cell proliferation (mean ± SEM, n = 3, ****p < 0.0001, Student’s t-test). (F) Necrotic area relative to total tumor area. Necrotic and normal areas quantified manually. (G) Quantification of mitotic figures in H&E-stained xenograft sections. For each tumor, 10 different fields of view were examined at high magnification (×40) (mean ± SEM, n = 7, ***p < 0.001, Student’s t-test).