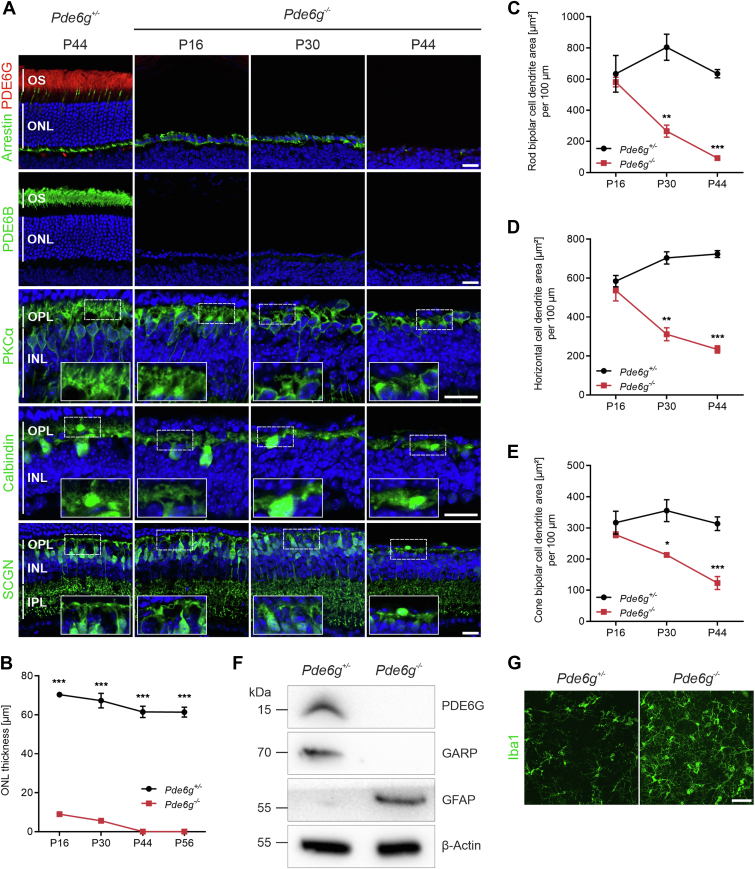
Figure 3.
Loss of phosphodiesterase 6 (PDE6G) results in rapid photoreceptor degeneration and retinal remodeling. A, Representative images of retinal sections immunolabeled for PDE6G (rod outer segment [OS]), cone arrestin (cones), PDE6B (rod OS), protein kinase C alpha (PKCα) (rod bipolar cells), calbindin (horizontal cells), and secretagonin (SCGN) (cone bipolar cells) and counterstained with Hoechst. B, Outer nuclear layer (ONL) thickness of mice at postnatal day (P) 16 (n = 2–3), P30 (n = 3), P44 (n = 3), and P56 (n = 3–4). Circles and squares, individual mice. Data, presented as the mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM), were compared by unpaired t test. ∗∗∗P < 0.001. C–E, Quantification of dendrite area from rod bipolar cells (C), horizontal cells (D), and cone bipolar cells (E) at P16 (n = 2–3), P30 (n = 3), and P44 (n = 4), respectively. Circles and squares, individual mice. Data, presented as the mean ± SEM, were compared by unpaired t test. ∗P < 0.03; ∗∗P < 0.002; ∗∗∗P < 0.001. F, Representative immunoblot of P30 retinal lysates. β-actin, loading control. G, Representative images of microglia/macrophages in the center of P44 flat-mounted retinas immunostained for ionized calcium-binding adapter molecule 1 (Iba1). Scale bars, 10 μm. GARP = glutamic-acid-rich protein; GFAP = glial fibrillary acidic protein; INL = inner nuclear layer; IPL = inner plexiform layer; kDa = kilodalton; OPL = outer plexiform layer.